- #1
Math Amateur
Gold Member
MHB
- 3,992
- 48
I am reading Joseph J. Rotman's book: Advanced Modern Algebra (AMA) and I am currently focused on Section 7.1 Chain Conditions (for modules) ...
I need some help in order to gain a full understanding of some remarks made in AMA on page 526 on modules in the context of chain conditions and composition series for modules ... ...
The remarks read as follows:
 My questions on this text are as follows:Question 1
My questions on this text are as follows:Question 1
In the above text we read:
" ... ... The Correspondence Theorem shows that a submodule N of a left R-module is a maximal submodule if and only if M/N is simple ... ... "
Can someone please explain exactly how the Correspondence Theorem leads to this result ... ?Question 2
In the above text we read:
" ... ... a left R-module is simple if and only if it is isomorphic to R/I for some maximal left ideal I ... ... "
Can someone please demonstrate, formally and rigorously why this is true ...?
Hope someone can help ...
Peter=================================================
The above post refers to the Correspondence Theorem for Modules which in Rotman's Advanced Modern Algebra is Theorem 6.22 ... I am therefore providing the text of Theorem 6.22 as follows:
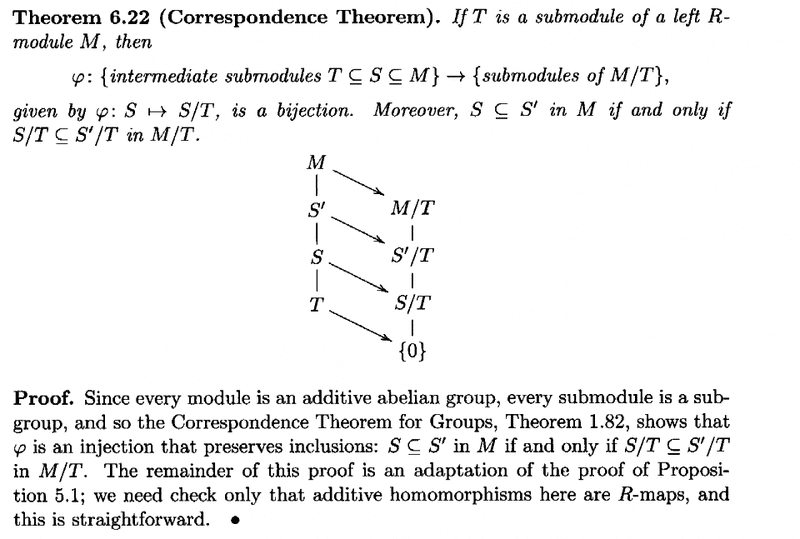
I need some help in order to gain a full understanding of some remarks made in AMA on page 526 on modules in the context of chain conditions and composition series for modules ... ...
The remarks read as follows:
In the above text we read:
" ... ... The Correspondence Theorem shows that a submodule N of a left R-module is a maximal submodule if and only if M/N is simple ... ... "
Can someone please explain exactly how the Correspondence Theorem leads to this result ... ?Question 2
In the above text we read:
" ... ... a left R-module is simple if and only if it is isomorphic to R/I for some maximal left ideal I ... ... "
Can someone please demonstrate, formally and rigorously why this is true ...?
Hope someone can help ...
Peter=================================================
The above post refers to the Correspondence Theorem for Modules which in Rotman's Advanced Modern Algebra is Theorem 6.22 ... I am therefore providing the text of Theorem 6.22 as follows:
