You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
What is Optics: Definition and 999 Discussions
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light. Because light is an electromagnetic wave, other forms of electromagnetic radiation such as X-rays, microwaves, and radio waves exhibit similar properties.Most optical phenomena can be accounted for by using the classical electromagnetic description of light. Complete electromagnetic descriptions of light are, however, often difficult to apply in practice. Practical optics is usually done using simplified models. The most common of these, geometric optics, treats light as a collection of rays that travel in straight lines and bend when they pass through or reflect from surfaces. Physical optics is a more comprehensive model of light, which includes wave effects such as diffraction and interference that cannot be accounted for in geometric optics. Historically, the ray-based model of light was developed first, followed by the wave model of light. Progress in electromagnetic theory in the 19th century led to the discovery that light waves were in fact electromagnetic radiation.
Some phenomena depend on the fact that light has both wave-like and particle-like properties. Explanation of these effects requires quantum mechanics. When considering light's particle-like properties, the light is modelled as a collection of particles called "photons". Quantum optics deals with the application of quantum mechanics to optical systems.
Optical science is relevant to and studied in many related disciplines including astronomy, various engineering fields, photography, and medicine (particularly ophthalmology and optometry). Practical applications of optics are found in a variety of technologies and everyday objects, including mirrors, lenses, telescopes, microscopes, lasers, and fibre optics.
View More On Wikipedia.org
Some phenomena depend on the fact that light has both wave-like and particle-like properties. Explanation of these effects requires quantum mechanics. When considering light's particle-like properties, the light is modelled as a collection of particles called "photons". Quantum optics deals with the application of quantum mechanics to optical systems.
Optical science is relevant to and studied in many related disciplines including astronomy, various engineering fields, photography, and medicine (particularly ophthalmology and optometry). Practical applications of optics are found in a variety of technologies and everyday objects, including mirrors, lenses, telescopes, microscopes, lasers, and fibre optics.
View More On Wikipedia.org
-

Objects in Optics: Image Formation Explained
Guys Just wanted to clarify one doubt When we consider image formation by objects We always assume there's a source of light present ,right?(because all real-point and extended objects can't always be luminous ) we also know that it's diffused reflection of light or scattering of incident light...- UchihaClan13
- Thread
-
- Tags
- optics
- Replies: 19
- Forum: Optics
-
G
[optics] How to transport light/image in narrow tube
Hello there! I'm new on the forum and english is not my first language. I'm working on an art project and I wonder if there's any mean by which I can transport the light from an illuminated scene across a small tube (let say not larger than 5 cm in diameter) and over some distance (let say 2...- gregMontreal
- Thread
- Replies: 8
- Forum: General Engineering
-

Other Which Optics Textbook is Best for Intermediate-Level Courses: Hecht or Fowles?
I'm reading Hecht's book on optics and am absolutely hating it. The derivations are not rigorous and have many, many holes. They use unnecessary presentations (no div-grad-curl presentation of M's equations and instead writing out each of the 100 derivatives involved explicitly). Horrible book...- davidbenari
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Optics
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Science and Math Textbooks
-
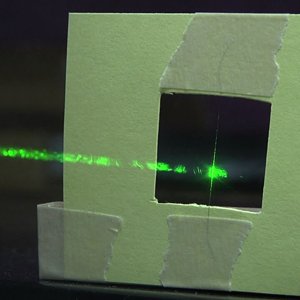
How to Measure the Width of a Hair With a Laser
This is a simple and fun experiment in optics for high school and intro college. Might even be a good incentive to get student to learn how to use a micrometer.- ZapperZ
- Media item
- optics
- Comments: 0
- Category: Experiments
-
S
Waves & Optics Homework: Polarization Through Weakly Scattering Fluid
Homework Statement An unpolarised light beam is shone horizontally through a cubic tank filled with weakly scattering fluid. Can vertically polarized light leave through the sides that are parallel to the beam’s propagation direction? Homework EquationsThe Attempt at a Solution My thinking is...- squeak
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Optics Waves Waves and optics
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
R
Is starlight a TEM00 gaussian beam or plane wave?
I am simulating a radio telescope and confused on what kind of source should I setup to simulate a star. Should it be a TEM00 gaussian beam or simply a plane wave?Cheers, Robin -
T
Displacement of virtual image problem
An object is within a glass sphere of radius R with a refractive index of 1.5 . I'm trying to calculate the displacement of the virtual object relative to the actual when viewed from the side, such that the refracted ray emanating from the object becomes horizontal. I would like to know S (the...- theguyoo
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
T
What is a floquet (optical) sideband?
In literature, I read:"(exposed in a beam of light) in floquet theory, the quasi-static eigenvalue spectrum at finite driving field A shows copies of the original bands shifted by integer multiples of ##\Omega##, the so-called Floquet sidebands" I have read something about floquet theory and...- taishizhiqiu
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Atomic and Condensed Matter
-

Visual Fire: An Analysis of the Greek Belief in Eye Emission and Its Flaws
I am reading the book "A History Of Optics" by Oliver Darrigol, and I came across this sentence (under the heading Visual Fire): Isn't this a low-quality argument? This can be directly disproved by the fact that humans inbabilty to see in dark, viz. if humans can see things from the "fire"...- Vinay080
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Other Physics Topics
-
L
Optics: Center of Fizeau Fringe? Michelson Interferometer
Hello everyone, i am simulating a Michelson interferometer, where one mirror is slightly tilted, see picture.. This results in circular arcs / hyperbolic cross-section fringes. The center of these fringes depends on the focal length i am using, see picture. Is there an analytical expression for... -
A
Optics : interference and diffraction
interference is a superposition of two waves coming two slits... diffraction is a superposition of a family of waves from a single slit.. then how the fringes formed during double slit experiment is actually a superposition of single-slit diffraction from each slit and the double-slit...- Abishek Balaji
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Optics
-
Atmospheric Optics: Moon 22° Halo & Paraselenic Circle
Took this image of the moon a couple of days ago. It shows the 22° halo and if you squint and imagine, part of the paraselenic circle. for more info: http://www.atoptics.co.uk/halo/common.htm- Andy Resnick
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Atmospheric Optics
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Optics
-
B
How does graded-index material reduce pulse spreading in optical fibres?
Homework Statement [/B] The textbook is talking about pulse spreading/dispersion in optical fibres. Book says: "The spreading of the pulse is due to two dispersion effects: (i) Chromatic dispersion occurs because the refractive index of the fibre is different for different frequencies...- Barclay
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
A
How optical axis is related to dielectric tensor?
I want to know the relationship between the optical axis direction of a crystal and the dielectric constants in different directions in an anisotropic material.- AAS
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
P
Undergraduate Math for Quantum Optics vs Particle Physics
I'm halfway through my junior year and I'm hoping to do Quantum Optics or Particle Physics in graduate school (I'm doing the recommended courses for both since I'm still undecided). Besides the math required from the physics major (ie. Calculus, linear algebra, ODEs, PDEs, complex analysis)...- PManslaughter
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: STEM Academic Advising
-
T
Anyone here with a physics Ph.D that specialized in Optics?
Hey everyone! I was wondering what the job prospects in academia and outside academia were like for people who have a physics Ph.D's specializing in optics? Were there a good number of STEM related choices or was it just as difficult as any other speciality? Thanks!- TroyElliott
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: STEM Career Guidance
-

What is the Jones Matrix of a mirror at an angle?
Hi, Concerning optical polarization, what is the Jones Matrix of a mirror at a non-zero angle of incidence with respect to incoming light? For a mirror at normal incidence the matrix is (1 0; 0 -1); How do I incorporate the angle? -
M
Project sharp shadows from LED
Using a high-power LED light (the surface mount kind, about 4x4mm with 120 degree viewing angle) I'd like to project shadows of a fine metal mesh onto a wall. I have tried various lens arrangements and found that placing a pinhole in front of the LED makes the sharpest shadows. This makes...- muffinator
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Classical Physics
-
T
Derivative of Axial Resolution from Rayleigh's Limit
I am currently studying optical microscope and discover that the axial resolution is limited as r(z) = 2pi / (NA)^2. However, while I got hints that it is due to the Rayleigh's limit, I can't derivative the equation using numerical method. It would be huge thanks if anyone can help me on the...- TS Wong
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Axial Derivative Limit Optics Resolution
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Classical Physics
-
A
Determine the intensity profile and fwhm for gaussian beam.
Homework Statement A beam of wavelength 600 nm has initially an intensity profile of Gaussian shape with a fwhm of 1 mm. Determine the intensity profile and fwhm 10 meter away.Homework Equations FWHM = λ/(2NA√(1 + I/Is)) The Attempt at a Solution [/B] FWHM1 = 1mm = 600 nm/(2NA√(1 + I/Is))...- Aerozeppelin
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
M
How can I find the minimum index of refraction?
Homework Statement We look at the center of one face of a solid cube of glass on a line of sight making 55° with the normal to the cube face. What is the minimum refractive index of glass for which you will see through the opposite face of the cube? (Hint: see through will be possible if the...- mbnMecha
- Thread
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
C
What Index of Refraction is Needed for a 104nm Coating to Cancel 550nm Light?
Homework Statement You are designing a thin transparent reflective coating for the front surface of a sheet of glass. The index of refraction of the glass is 1.52 and when it is in use, the coated glass has air on both sides. Because the coating is expensive, you want to use a layer that has...- Callix
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Film Light Optics Reflection Waves
- Replies: 10
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
E
Cross Phase Modulation in Optical Fibers (Fiber Optics)
Hello everyone. I have been practicing for my exam in fiber optics, and stumbled upon the following question: We have a transmission system with 3 channels, composed of a single mode fiber and a dispersion compensation fiber. Specifications are given for each. We need to calculate the channel's... -
A
Find the axial resolution achieved for confocal microscope
Homework Statement 2. Homework Equations F-number is f/d x0 = 1.2λ(fnumber) The Attempt at a Solution [/B] Fnumber1 = 0.2 Fnumber2 = 0.6 x01 = 180nm x02 = 540nmThese values seem large for depth resolution, is this correct?- Aerozeppelin
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Axial Lens Microscope Optics Resolution
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
P
Second order correlation function for non ideal laser
Hi, it is known that second order correlation function (g2) is a constant( =1) for ideal laser or single frequency light sources. So, what is the second order correlation function for non ideal laser? Is it still a constant or something related to the coherence time of the laser?- pumpkin
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Atomic and Condensed Matter
-
J
Violation of Bell inequalities for classical fields?
There is a recent article (Optics July 2015) claiming violation of Bell inequalities for classical fields: "Shifting the quantum-classical boundary: theory and experiment for statistically classical optical fields" https://www.osapublishing.org/optica/abstract.cfm?URI=optica-2-7-611...- jarekduda
- Thread
- Replies: 70
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
L
How to use the b&h tcspc in experments of quantum optics?
Hi everyone, There is a b&h Time-Correlated Single Photon Counting (tcspc, spc-130) in our lab, and I use it for coincidence of spdc in quantum optics. Actually I know some about how it work, but when it comes to parameter setting of the software I know nothing. Recently, I read some paper...- liuray
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-

What happens if I have a rotating half-wave plate?
Hey there, What would happen if I had a half-wave plate, and I rotated it at like 1 Hz? If I stick a linear polarizer on the other end, what would my outcoming beam look like if the incoming one was natural light? -
R
Need Aspherical Lens Equation (+20d, 55mm)
Hello. I am not related to physics or any optics related field. I am in need of equation for +20d aspherical lens of diameter 55mm. Can anybody help me?- Raza121
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Convex lens Lens Optics
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Optics
-
J
Classical Waves (and maybe optics) problems book
I want to practice my problem solving skills on waves(and optics) so, I would like to have a good problems book about waves(not a book containing problems-nearly every book contains problems- but a book that is all about the problems). I am looking for a book which has exercises that offer...- Joker93
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Science and Math Textbooks
-

What are localised and non localised fringes?
what does it mean by localisation of fringes?- pratikaman
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Fringes Interference Optics
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Other Physics Topics
-
A
Geometrical Optics: Image Position with No Principal Axis
What would be the position an image formed by a Lens or a mirror if the object is not kept on the principal axis? -

Calculate the desired incident polarization of a light beam
Hi I want to calculate the necessary incident polarization of a light beam at a given angle of incidence (theta_i) that reflects off BK7 glass (n = 1.5168) and is linearly polarized (i.e., 45 degrees). I know how to do similar calculations for incident natural unpolarized light, but not in the... -
A
Why Don't Spherical Waves Interfere: Exploring Huygens Principle
Hi according to Huygens principle every point on the wave front acts as a spherical source. so if a we emit monochromatic light on a screen without passing light from grating, we should see interference pattern but we don't. why don't these spherical waves interfere with each other? is this...- alikazemi7
- Thread
- Replies: 18
- Forum: Classical Physics
-
P
Geoemtrical Optics: Principal Plane question
Homework Statement An equiconvex lens having spherical surfaces of radius 10cm, a central thickness of 2cm, and a refractive index of 1.61 is situated between air and water (n=1.33). An object 5cm high is placed 60cm in front of the lens surface. Find the cardinal points for the lens and the...- Potatochip911
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
P
Wave Optics: Electromagnetic Waves
" Thus according to Maxwell, light waves are associated with changing electric and magnetic fields; changing electric field produces a time and space varying magnetic field and a changing magnetic field produces a time and space varying electric field. The changing electric and magnetic fields...- Prannoy Mehta
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
A
Schools Optics for High School Senior at Ohio State Univ.
I'm a high school senior taking classes at Ohio State University. I'm currently enrolled in Basic Astrophysics and Planetary Astronomy, and have already decided to take Stellar, Galactic, & Extragalactic Astronomy & Astrophysics (wow that is LONG!) next semester. I've been looking at other...- Astro Student
- Thread
-
- Tags
- High school Optics School
- Replies: 2
- Forum: STEM Academic Advising
-
C
Complex Degree of Coherence (Cittert-Zernike)
Homework Statement A light source consists of two long thin parallel wires, separated by a distance, W. A current is passed through the wires so that they emit light thermally. A filter is placed in front of the wires to only allow a narrow spectral range, centred at λ to propagate to a... -
P
Why are images formed when rays intersect?
In most (perhaps all) books it was mentioned that intersection of the light from the object when reflected by the mirror or refracted by a lens intersect at a particular point. That point when traced till the principal axis gives the image. (Provided object lies on the axis). I do not understand...- Prannoy Mehta
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Formation Image Optics Ray Ray optics
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Optics
-
B
Interaction of Gaussian Beams with Optics
Homework Statement In a youtube video() it is explained how gaussian beams propagate through an optical lens. Using the complex parameter q \frac{1}{q} = \frac{1}{R} - \frac{j\lambda}{\pi n w^2} (with R the radius of curvature), one can use the ABCD matrix to calculate the effect of an optical...- barefeet
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Beams Gaussian Interaction Optics
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
G
How Do You Calculate the System Matrix for a Lens After a Beam Waist?
Homework Statement A thin lens is placed 2m after the beam waist. The lens has f = 200mm. Find the appropriate system matrix. This is a past exam question I want to check I got right. Homework Equations For some straight section [[1 , d],[0 , 1]] and for a thin lens [[1 , 0],[-1/f , 1]]...- girlinphysics
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-

Snell's law for an interface with variable refractive index
Consider an interface along x-axis which separates two media. The medium below y = 0 is air or vacuum and light is incident from this medium onto the surface. The refractive index of the medium above y = 0 varies with x as some function of x : μ = f(x). Does the Snell's law still hold good ?? If...- Vaibhav Sahu
- Thread
- Replies: 13
- Forum: Optics
-
P
What is the true nature of white light?
Hi, I studied 'A' level physics back in the '80s, my dad was a physics teacher, and I have an ongoing interest in the subject. I'm particularly interested in optics. The main thing that I remember being taught incorrectly at school is that white light is a combination of red, green, and blue...- PhilHibbs
- Thread
-
- Tags
- introduction optics
- Replies: 1
- Forum: New Member Introductions
-

Optics and waves, mirage. University physics
Mirage: we consider the x-y plane describing vertical y and horizontal x directions, with an inhomogeneous index of refraction n(y). In this case, using calculus of variations, Fermat’s principle for the trajectory of a ray of light may be re-written as n(y)/√1+(dy/dx)^2 = A. Where A is a real...- YogiBear
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
J
Light Polarization and Jones Matrices
Light reflecting off a mirror actually penetrates a short distance into the mirror surface material. In metals, this distance is very short (much less than a wavelength) and so can be neglected. But metals tend to also absorb ~10% of the light, which is undesirable. Today’s modern multilayer...- jjjefjrdcb
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Light Matrices Optics Polarization
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
H
...review article on atom optics - need recommendation.
Before life got in the way I used to follow this field as a science fan up until the early 90's. Any good review articles for a general readership that can fill the gap in from early 90's till now. I would like to see how a lot of that research progressed and if any applications / devices came...- houlahound
- Thread
-
- Tags
- article Atom Optics Recommendation
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Atomic and Condensed Matter
-
W
Geometric optics and Fermat's principle
Homework Statement A ray travels as shown in the image attached below. In this case, Fermat's principle may be written as ##A =\frac{n(1+ay)}{\sqrt{1+(y')^2}}## Where y' is dy/dx, n is the index of refraction and A is a real constant. The trajectory of a ray of light is given by ##y =...- whatisreality
- Thread
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
Quit undergrad physics -- Wishes and options? Advice please
Hello everyone, I am brand new here in the PhysicsForum and this is my very first message. So it's apleasure to meet likeminded people sharing the same interest and probably also profession. The latter is also the reason why I finally registered in this forum and I sincerely hopethat I am given...- pioneerboy
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: STEM Career Guidance
-
E
When is a Numerical Aperture considered High?
When will you consider that the numerical aperture is high? I was told that the numerical Angular Spectrum Method is only valid low numerical aperture values, I want to know the boundary of this value. Thank you in advance.- ecastro
- Thread
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Other Physics Topics
-

Possible non-burning visible beam mock-up?
To give a little idea for what I'm aiming for: I want to make a prop laser gun. It doesn't have to actually do anything, but I've decided it'd be awesome if it did. I could use a 2-5W blue laser diode like some people who make awesome contraptions with lasers show on YouTube, but I'd frankly...