- #1
gregMontreal
- 4
- 0
Hello there!
I'm new on the forum and english is not my first language.
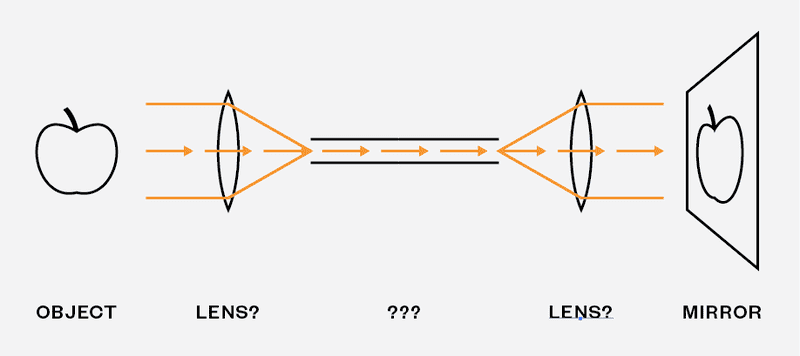
I'm working on an art project and I wonder if there's any mean by which I can transport the light from an illuminated scene across a small tube (let say not larger than 5 cm in diameter) and over some distance (let say 2 meters) and restitute that light on a large mirror.
Please see my image below.
Thank you!
I'm new on the forum and english is not my first language.
I'm working on an art project and I wonder if there's any mean by which I can transport the light from an illuminated scene across a small tube (let say not larger than 5 cm in diameter) and over some distance (let say 2 meters) and restitute that light on a large mirror.
Please see my image below.
Thank you!