- #1
johnconnor
- 62
- 0
Below 20K, The specific heat capacity c of silver varies with temperature according to the equation[tex]c/\text{J /kg /K} = 1.5x10^{-4}(T/K)^3 + 6.0x10^{-3} T/K[/tex].
If a small silver sphere of diameter 4am and at 20K is placed in 25g of liquid helium at 4K, what fraction of the liquid will evaporate?
[Density of silver = 1.05E4 kg/m^3, specific latent heat of vaporisation of helium = 2.1E4 J/kg; boiling point of helium = 4K]
[expand=Attempt]
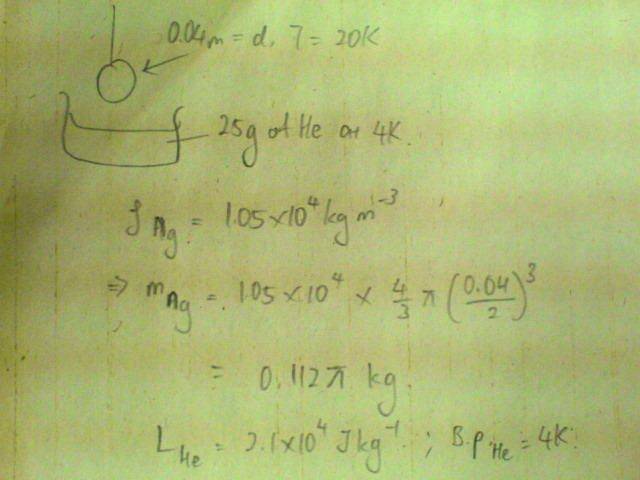
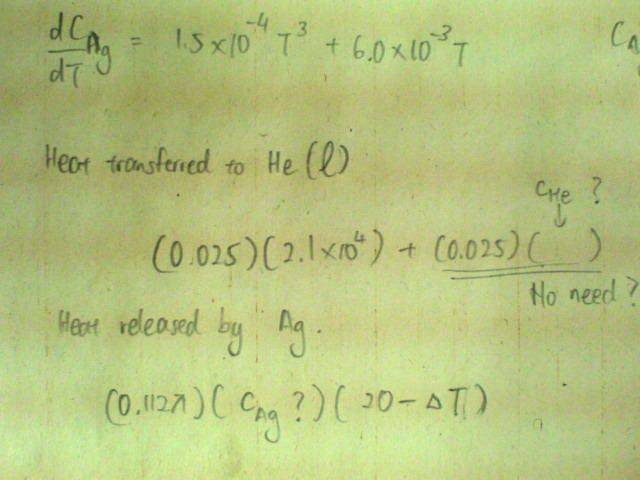
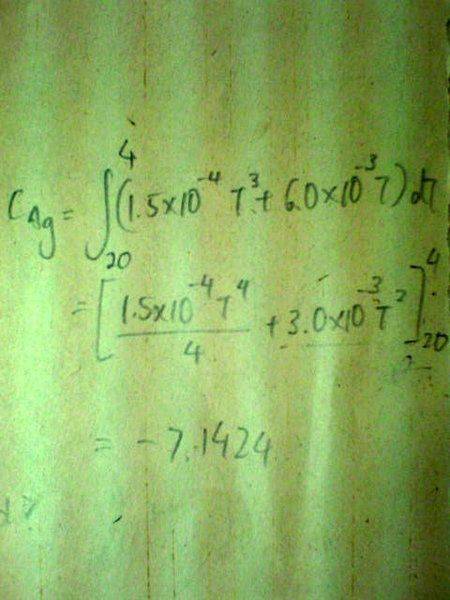
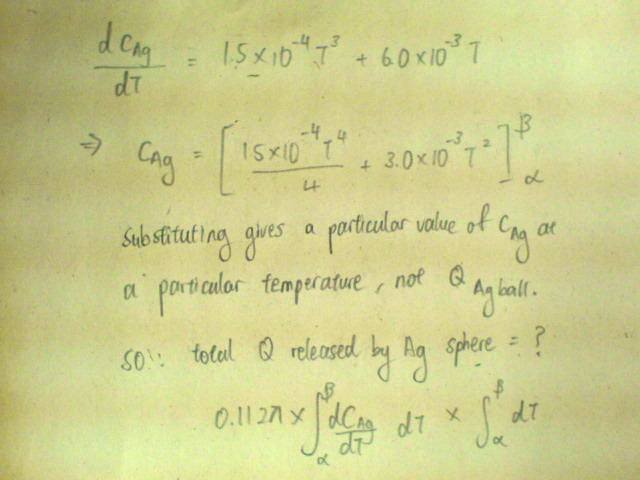 [/expand]
[/expand]
And I'm stuck. The answer is 1/210. I think my mistake is not considering the "combined effect" (if there's one?) of the silver sphere with the helium liquid, but I'm not very sure how do I express that in mathematical form.
Any help is appreciated. Thank you!
If a small silver sphere of diameter 4am and at 20K is placed in 25g of liquid helium at 4K, what fraction of the liquid will evaporate?
[Density of silver = 1.05E4 kg/m^3, specific latent heat of vaporisation of helium = 2.1E4 J/kg; boiling point of helium = 4K]
[expand=Attempt]
And I'm stuck. The answer is 1/210. I think my mistake is not considering the "combined effect" (if there's one?) of the silver sphere with the helium liquid, but I'm not very sure how do I express that in mathematical form.
Any help is appreciated. Thank you!