- #1
BigKevSebas
All variables and given/known data and Relevant equations:
So I got the functions for a bottle design (one side with the bottle lying horizontally):
1. y=-1/343x^3+3/98x^2 + 2.5 ; 0<x<7
2. y=3; 7<x<15
3. y=-1/98x^2+15/49x+69/98; 15<x<22
Combined they give the volume of 570.2mL using the volume revolution equation:
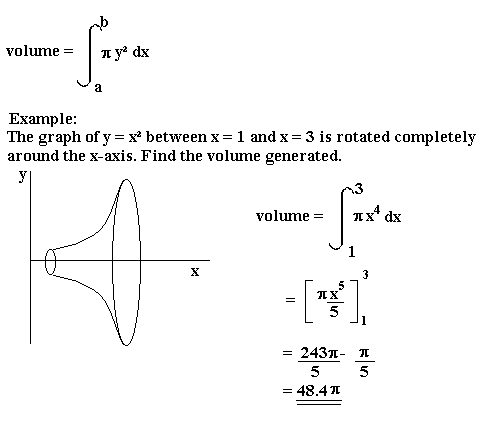
I need to rescale the functions above so that I get half the volume. I simply can't reduce the length of the functions by half, as the new curves have to be a similar shape to the original one. Therefore I need to reduce the radius and length at the same time.
The attempt at a solution
I know I have to multiply the function by 1/2^(1/3). To do this I had to convert function 3 to the vertex form, and I got
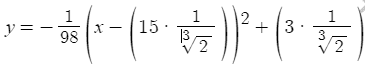 , as the new rescaled function 3.
, as the new rescaled function 3.
Furthermore, I also got,
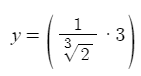 as the new function of 2.
as the new function of 2.
The problem:
I'm stuck on rescaling function 1, as I can't convert it to a vertex form. I have tried the method from 'https://www.enotes.com/homework-help/how-convert-cubic-equation-standard-form-ax-2-bx-2-312067' but that has not worked. Any ideas how I would be able to rescale function 1.
So I got the functions for a bottle design (one side with the bottle lying horizontally):
1. y=-1/343x^3+3/98x^2 + 2.5 ; 0<x<7
2. y=3; 7<x<15
3. y=-1/98x^2+15/49x+69/98; 15<x<22
Combined they give the volume of 570.2mL using the volume revolution equation:
I need to rescale the functions above so that I get half the volume. I simply can't reduce the length of the functions by half, as the new curves have to be a similar shape to the original one. Therefore I need to reduce the radius and length at the same time.
The attempt at a solution
I know I have to multiply the function by 1/2^(1/3). To do this I had to convert function 3 to the vertex form, and I got
Furthermore, I also got,
The problem:
I'm stuck on rescaling function 1, as I can't convert it to a vertex form. I have tried the method from 'https://www.enotes.com/homework-help/how-convert-cubic-equation-standard-form-ax-2-bx-2-312067' but that has not worked. Any ideas how I would be able to rescale function 1.