- #1
Noora Alameri
- 12
- 0
Hey everybody,
I am trying to expand a system of seven qubits from one dimensional Hamiltonian to the two dimensional representation.
I have the one dimensional representation and I don't know what to add to transform it from 1D to 2D representation.
I would really appreciate your help and guidance.
Here is my !D Hamiltonian:
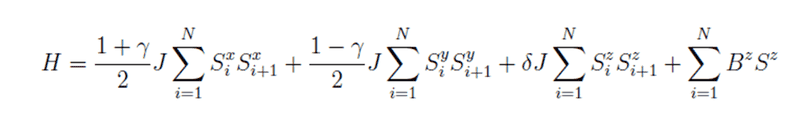 Thank You,
Thank You,
Noora
I am trying to expand a system of seven qubits from one dimensional Hamiltonian to the two dimensional representation.
I have the one dimensional representation and I don't know what to add to transform it from 1D to 2D representation.
I would really appreciate your help and guidance.
Here is my !D Hamiltonian:
Noora