- #1
ichabodgrant
- 49
- 0
Hi, normally when we try to analyse a structural beam with composite section, we apply transformed section method or so. But what if two beams are just put together (one onto another one) instead of having a composite relation (e.g. glued together), how am I going to analyse the forces and stresses?
Someone tells me to separately consider the two beams. But how will the action load change for the two beams? Is there any shear stress that needs be to considered in the interface between the two beams?
(in the following graph, it is a simply supported beam. Let's think beam A and B are of equal length, equal thickness and same cross-section. But they are not in a composite manner, just put together. And let's say it is given the required allowable bending stresses, Young's moduli for both beams, how am I going to interpret these for such a non-composite beam? What are the differences compared to that when I see it as a composite beam?)
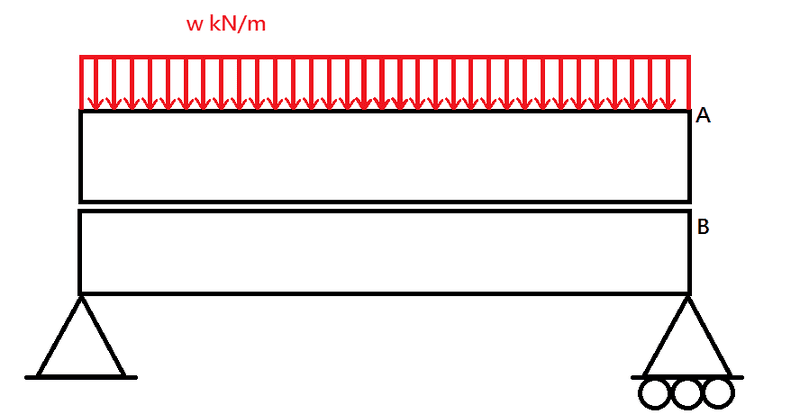
Someone tells me to separately consider the two beams. But how will the action load change for the two beams? Is there any shear stress that needs be to considered in the interface between the two beams?
(in the following graph, it is a simply supported beam. Let's think beam A and B are of equal length, equal thickness and same cross-section. But they are not in a composite manner, just put together. And let's say it is given the required allowable bending stresses, Young's moduli for both beams, how am I going to interpret these for such a non-composite beam? What are the differences compared to that when I see it as a composite beam?)