- #1
FeDeX_LaTeX
Gold Member
- 437
- 13
Kinematics -- Vector DE

Here's their solution.
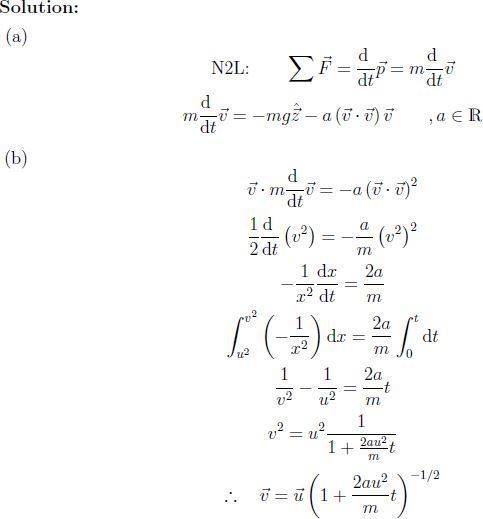
I'm stuck on (b). The first and second lines are fine. But how do they get from the second line to the third line? And then in the fourth line, why are they integrating from u^2 to v^2?
EDIT: Sorry for the image size.
Homework Statement
The Attempt at a Solution
Here's their solution.
I'm stuck on (b). The first and second lines are fine. But how do they get from the second line to the third line? And then in the fourth line, why are they integrating from u^2 to v^2?
EDIT: Sorry for the image size.