- #1
roldy
- 237
- 2
1. For each of the following equations, state the order and whether it is nonlinear, linear inhomogeneous, or linear homogeneous; provide reasons.
(a) ut-uxx+1=0
(b) ut-uxx+xu=0
(c) ut-uxxt+uux=0
(d) utt-uxx+x2=0
(e) iut-uxx+u/x=0
(f) ux(1+u2x)-1/2+uy(1+u2y)-1/2=0
(g) ux+eyuy=0
(h) ut+uxxxx+(1+u)-1/2=0
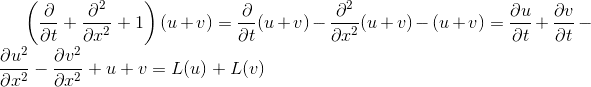
there it is linear
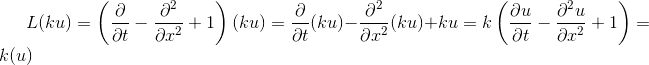
therefore it is nonhomogeneous
I think I have the method down but I tried (c) and the book gave a different answer...
(c) linear homogeneous
the book says it's just linear, this is where I don't understand.
(a) ut-uxx+1=0
(b) ut-uxx+xu=0
(c) ut-uxxt+uux=0
(d) utt-uxx+x2=0
(e) iut-uxx+u/x=0
(f) ux(1+u2x)-1/2+uy(1+u2y)-1/2=0
(g) ux+eyuy=0
(h) ut+uxxxx+(1+u)-1/2=0
there it is linear
therefore it is nonhomogeneous
I think I have the method down but I tried (c) and the book gave a different answer...
(c) linear homogeneous
the book says it's just linear, this is where I don't understand.