- #1
Ashish GK
Hello everyone,
I am Ashish, a mechanical engineering graduate from Arizona. I am doing a case study on some of the design related flaws in a high purity germanium detector. The information and pictures that I am posting is of an old detector from one of the manufacturers and it is currently not being sold in the market.
There is a cylindrical germanium crystal that is clamped to a vertical copper rod. At the clamping end, the crystal is mechanical supported by a stack of clear plates that fit tightly into the bore of the detector's endcap. The set up is shown in the following figure:

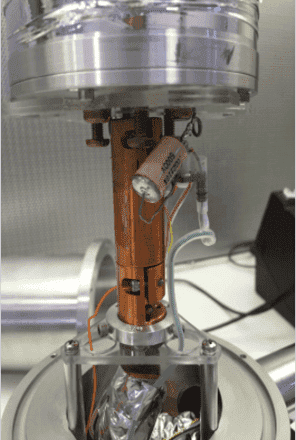
(a) (b)
I am trying to redesign the geometry of the stack of plates. This is because in the existing design, a lot of machining work has to be done and there are sharp edges. The crystal must be kept as cold as possible. Hence, the entire setup is connected to a 30 L liquid nitrogen dewar while running. The material is Plexiglas and sometime results in the formation of minor cracks, which I feel could be due to thermal cycling.
I would like to get your suggestions on redesigning the geometry of the plates that mechanically support the crystal. I am also trying to understand other flaws with this existing design (other than the material cracking). Hence, it would also be helpful if you can provide your suggestions on any other limitation in this design.
Thanks,
Ashish
I am Ashish, a mechanical engineering graduate from Arizona. I am doing a case study on some of the design related flaws in a high purity germanium detector. The information and pictures that I am posting is of an old detector from one of the manufacturers and it is currently not being sold in the market.
There is a cylindrical germanium crystal that is clamped to a vertical copper rod. At the clamping end, the crystal is mechanical supported by a stack of clear plates that fit tightly into the bore of the detector's endcap. The set up is shown in the following figure:
(a) (b)
I am trying to redesign the geometry of the stack of plates. This is because in the existing design, a lot of machining work has to be done and there are sharp edges. The crystal must be kept as cold as possible. Hence, the entire setup is connected to a 30 L liquid nitrogen dewar while running. The material is Plexiglas and sometime results in the formation of minor cracks, which I feel could be due to thermal cycling.
I would like to get your suggestions on redesigning the geometry of the plates that mechanically support the crystal. I am also trying to understand other flaws with this existing design (other than the material cracking). Hence, it would also be helpful if you can provide your suggestions on any other limitation in this design.
Thanks,
Ashish