- #1
tolove
- 164
- 1
I'm not entirely sure on the properties of limits, but this seems to work. Could someone look over this for me?
http://imgur.com/6zCHYo5
http://imgur.com/6zCHYo5
tolove said:I'm not entirely sure on the properties of limits, but this seems to work. Could someone look over this for me?
http://imgur.com/6zCHYo5
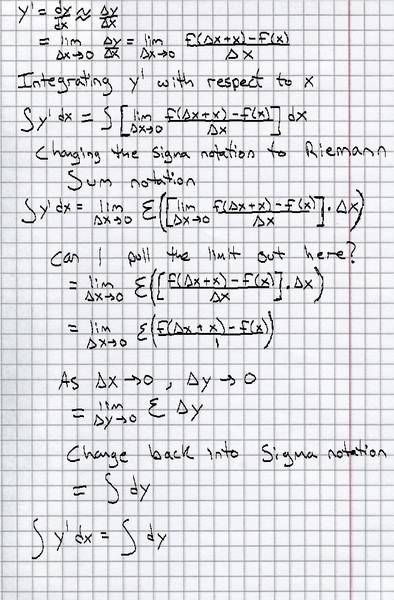
SammyS said:What is it that you're trying to do?
Please state the problem.
tolove said:Not really a problem here, just wanting to make sure I'm doing this correctly. I'm trying to show that ∫ y' dx = ∫ dy through definitions.
A limit is a value that a function or sequence approaches as the input or index value gets closer and closer to a specific value, typically denoted as x approaches a or n approaches a, respectively.
A limit is the value that a function approaches, while the value of a function at a specific point is the actual output of the function at that point. In other words, a limit is the expected value of the function as the input approaches a certain value, but it may not always be equal to the actual value of the function at that point.
A one-sided limit only considers the behavior of a function as the input approaches a specific value from either the left or right side. A two-sided limit, on the other hand, considers the behavior of the function as the input approaches the specific value from both the left and right sides.
Yes, a limit can exist even if the function is not defined at that point. This is because a limit only looks at the behavior of the function as the input approaches a specific value, not necessarily the value of the function at that point. However, it is important to note that if a limit exists, it does not necessarily mean that the function is defined at that point.
Some common properties of limits include the sum, difference, product, and quotient rules, as well as the power and root rules. These properties allow us to simplify and evaluate limits algebraically without having to rely on graphical or numerical methods.