- #1
carlyn medona
Homework Statement
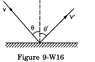
A ball of mass m hits the floor with a speed v making
an angle of incidence theta with the normal. The coefficient
of restitution is e. Find the speed of the reflected ball and
the angle of reflection of the ball.
The Attempt at a Solution
I know that momentum is conserved in x direction. so I got one equation.
Now how do I use e in this problem[/B]