You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
What is Entropy: Definition and 1000 Discussions
Entropy is a scientific concept, as well as a measurable physical property that is most commonly associated with a state of disorder, randomness, or uncertainty. The term and the concept are used in diverse fields, from classical thermodynamics, where it was first recognized, to the microscopic description of nature in statistical physics, and to the principles of information theory. It has found far-ranging applications in chemistry and physics, in biological systems and their relation to life, in cosmology, economics, sociology, weather science, climate change, and information systems including the transmission of information in telecommunication.The thermodynamic concept was referred to by Scottish scientist and engineer Macquorn Rankine in 1850 with the names thermodynamic function and heat-potential. In 1865, German physicist Rudolph Clausius, one of the leading founders of the field of thermodynamics, defined it as the quotient of an infinitesimal amount of heat to the instantaneous temperature. He initially described it as transformation-content, in German Verwandlungsinhalt, and later coined the term entropy from a Greek word for transformation. Referring to microscopic constitution and structure, in 1862, Clausius interpreted the concept as meaning disgregation.A consequence of entropy is that certain processes are irreversible or impossible, aside from the requirement of not violating the conservation of energy, the latter being expressed in the first law of thermodynamics. Entropy is central to the second law of thermodynamics, which states that the entropy of isolated systems left to spontaneous evolution cannot decrease with time, as they always arrive at a state of thermodynamic equilibrium, where the entropy is highest.
Austrian physicist Ludwig Boltzmann explained entropy as the measure of the number of possible microscopic arrangements or states of individual atoms and molecules of a system that comply with the macroscopic condition of the system. He thereby introduced the concept of statistical disorder and probability distributions into a new field of thermodynamics, called statistical mechanics, and found the link between the microscopic interactions, which fluctuate about an average configuration, to the macroscopically observable behavior, in form of a simple logarithmic law, with a proportionality constant, the Boltzmann constant, that has become one of the defining universal constants for the modern International System of Units (SI).
In 1948, Bell Labs scientist Claude Shannon developed similar statistical concepts of measuring microscopic uncertainty and multiplicity to the problem of random losses of information in telecommunication signals. Upon John von Neumann's suggestion, Shannon named this entity of missing information in analogous manner to its use in statistical mechanics as entropy, and gave birth to the field of information theory. This description has been proposed as a universal definition of the concept of entropy.
View More On Wikipedia.org
Austrian physicist Ludwig Boltzmann explained entropy as the measure of the number of possible microscopic arrangements or states of individual atoms and molecules of a system that comply with the macroscopic condition of the system. He thereby introduced the concept of statistical disorder and probability distributions into a new field of thermodynamics, called statistical mechanics, and found the link between the microscopic interactions, which fluctuate about an average configuration, to the macroscopically observable behavior, in form of a simple logarithmic law, with a proportionality constant, the Boltzmann constant, that has become one of the defining universal constants for the modern International System of Units (SI).
In 1948, Bell Labs scientist Claude Shannon developed similar statistical concepts of measuring microscopic uncertainty and multiplicity to the problem of random losses of information in telecommunication signals. Upon John von Neumann's suggestion, Shannon named this entity of missing information in analogous manner to its use in statistical mechanics as entropy, and gave birth to the field of information theory. This description has been proposed as a universal definition of the concept of entropy.
View More On Wikipedia.org
-
T
What is the change in entropy?
Homework Statement A system with 100,000 molecules has 2 energy levels, A and B. At first, the 2 energy levels are populated equally. After a reversible process, energy level A is populated by 65% of the molecules and the system is at 293K. a) What is the difference in energy between the two...- tahaha
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Biology and Chemistry Homework Help
-
U
Understanding entropy generation
Hi all, I've been doing some pretty complex problems on closed systems in thermodynamics, and a few questions pooped up in my mind about Sgen (entropy generation). Please help me out with them.. 1. When work is done on a system (like a paddle wheel in a cylinder containing gas), there is...- Urmi Roy
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Entropy Generation
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Thermodynamics
-
F
Entropy limit inside event horizons
As I understand it, the entropy inside a horizon, the black hole event horizon or the cosmological event horizon, is limited by the entropy proportional to the surface area of that horizon. My question is: does that entropy limit always allow the possibility for maximum entropy of the material...- friend
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Beyond the Standard Models
-
L
Understanding Entropy: What is it?
I know this is elementary, but I'm having trouble understanding the definition of entropy. If someone could better clarify the term for me it would be much appreciated.- ls1datson
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Entropy
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Thermodynamics
-
O
Exploring Protein Entropy: The Curious Case of Collagen Binding to Bone
When collagen binds to bone, the entropy of the system increases. Why does the entropy not decrease, since it seems more logical that the entropy decreases since it seems to become more ordered?- ohshiznit422
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Thermodynamics
-
I
Re: Entropy - Actually a question about working in Polar Coordinates
show that \frac{d\hat{r}}{dt}=\hat{θ}\dot{θ} also, \frac{d\hat{θ}}{dt}=-\dot{θ}r i've tried finding the relationship between r and theta via turning it into Cartesian coord.s, and I've tried the S=theta r but still no luck. S=theta r dS/dt=d(theta)/dt r which is similar to the RHS...- iScience
- Thread
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
H
Definition of Entropy for Irreversible Processes
What is the definition of entropy of a thermodynamic irreversible process? In the case of reversible process from initial state 'a' to final state 'b' ,one may define entropy by 1) Constructing infinitely many reservoirs having temperatures corresponding to the temperature at every...- Hummel
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Definition Entropy
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Thermodynamics
-
R
High School Physics Competition: Change in Entropy
During a physics competition, I came across this question. My work was \begin{align*}\Delta S &= \frac{Q}{T} \\ \Delta S &= \frac{1.25 \times 10^3 \, \mathrm{J}}{348 \, \mathrm{K}} \\ \Delta S &= 3.59 \,\,\mathrm{\left( J/K\right )} \end{align*} but I was stuck in between two answer choices...- ReneG
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
D
Show extremum of the Entropy is a maximum
Homework Statement The Entropy of a probability distribution is given by, S = -k_B \sum _{i=1}^N p(i)\ln{p(i)} I've shown that the extremum of such a function is given by, S' = k_B \ln{N} (which is a positive quantity) Now I want to show that this is a maximum by showing that S' - S...- dipole
- Thread
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
K
Understanding Entropy and Free Falling Objects in a Vacuum System
Dear sir, Hi, Everyone. I have a question about entropy. If the object falls without air resistant (vacuum system) , Is entropy changed? If ΔS=0, it means reversible, is it possible that the object can go back to the original height? I know that it is impossible but can we explain that ΔS...- kimpantip
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Thermodynamics
-
D
How Is Entropy Calculated in Different Macrostates of Einstein Solids?
This is the problem: Consider a system of two Einstein solids, with NA = 300, NB = 200, and qtotal = 100. Compute the entropy of the most likely macrostate and of the least likely macro state. I only have a doubt. Is the most likely macro state when each solid has half the energy (in this...- d2x
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
B
Calculating Gibbs Free Energy w/o Standard Entropy
This is for my Chemical Engineering class, but it comes down to a thermodynamics question. I need to calculate the gibbs free energy for a few reactions, problem is some of the compounds (1-Buten-3-yne and Styrene) do not have standard entropy values that I can find. Without a standard entropy I...- bg93
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Thermodynamics
-
S
Entropy of Ideal Mixture Proof
Homework Statement Explain why, for an ideal mixture, the mixing entropy is given by ΔSmixing = k ln( Binomial Coefficient ( N, NA ) where N is the total number of molecules and NA is the number of molecules of type A. Use Stirling's Approximation to show that this expression is the same as...- superspartan9
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
J
Maximal Entropy Random Walk - quantum corrections to stochastic models
Imagine there is a complex system and we are interested in its basic statistical properties, like the stationary probability distribution. For example for a single electron wandering in defected lattice of semiconductor. Physics offers two basic ways of answering such question: - from one side...- jarekd
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
M
Delocalisation stability - primarily an entropy or enthelpy issue?
This question was prompted by reflecting after reading the standard textbook explanation that "the greater acidity of RCOOH vs ROH is due to the greater stability of the delocalised RCOO- ion causing the position of equilibrium to be further to the right". The equilibria can be written as...- Miffymycat
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Chemistry
-

Small scale entropy and information loss
I'm struggling to understand the implications and origins of the 2nd law. Entropy is such a slippery subject. Wikipedia has many many definitions of entropy. I've been studying Professor Susskind physics lectures, so I'm most interested in his favorite definition: that information is...- anorlunda
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Entropy Information Loss Scale
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Thermodynamics
-
K
Thermodynamics: Explaining Entropy for KiltedEngineer
I am a mechanical engineering student, but have yet to take thermodynamics. For months now, I have been reading up on thermo and am actually quite interested in it. However, I am still quite confused with the concept of entropy. Its pretty much the consencus that the "disorder" explanation is...- KiltedEngineer
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Entropy
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Mechanical Engineering
-
I
Light & Entropy: Will Photon Energy Last Forever?
Ok so the thread I was looking at is closed and I cannot pose this question there. The question was posed if light will travel forever or if it will degrade over time and the answers that were given were a bit incomplete. Here is a link to that thread...- Igottaknow
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Thermodynamics
-
T
Entropy of a black hole after evaporation
Black holes have an entropy, but they evaporate. At the end of the evaporation, the entropy is greater than the entropy at the beginning of the evaporation. I am looking for an example of a quantitative result for the entropy of the black hole after evaporation (or the entropy difference...- trimok
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Black hole Entropy Evaporation Hole
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Beyond the Standard Models
-
N
Entropy in polytropic processes
Homework Statement I have question on entropy for which I have no idea about, please help me out... a) Change of entropy of a gas is given with usual notations by: s2-s1=cvln(T2/T1)+Rln(V2/V1) using this relationship, show that for a polytropic process, entropy change can be expressed as...- nvjnj
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Entropy Polytropic
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Engineering and Comp Sci Homework Help
-
R
Finding the equations of state for a system (entropy)
Homework Statement Suppose the entropy of a system is given by the relation: S(E,V,N) = a(E,V,N)^(1/3) Determine three equations of state for this system Homework Equations there were no equations given on the sheet but I'm assuming that this might help...- ragnarokmonk
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
5
How are Entropy and Temperature conjugate variables?
Can someone conceptually explain to me how Temperature and Entropy are conjugate variables? I would imagine that Temperature and Internal Energy would be more appropriate, as I understand Heat flow causes changes in Internal Energy, some of which is used to change the translational motion of...- 541099
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Thermodynamics
-
N
Proof of subadditivity of quantum entropy
I'm having problems understanding the trace of tensor products when the density matrix is expressed in its reduced density operators. The proof of subadditivity is quite simple. S(ρAB||ρA\otimesρB) = Tr(ρABlogρAB) - Tr(ρABlogρA\otimesρB) = TrAB(ρABlogρAB) - Tr(ρAlogρA) - Tr(ρBlogρB) This...- Narvalen
- Thread
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
J
Is Time a Construct of Consciousness? Examining Entropy and the Reality of Time
Apologies if this is in the wrong forum: I am reading Biocentrism by Robert Lanza, and one of his arguments is that time has no real existence outside of animal perception. He says is is the process by which we perceive changes in the universe. The books argument is that everything is a...- JordanSC5
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
M
What is the entropy of the quantum state vacuum in inflationary theory
Consider the vacuum state that is hypothesised to precede the moment of inflation in classical inflationary theory. The theory assumes that quantum fluctuations in this vacuum are magnified because of the process of inflation and have gone on to form the real energy structures that we witness...- Maximise24
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
M
Entropy of a vacuum and heat death of the universe
According to the third law of thermodynamics, one could argue that a vacuum has zero entropy, since it has only one ground state and a temperature at absolute zero. However, assuming the accelerated expansion of the universe to result in a 'heat death', i.e. a state of absolute thermal...- Maximise24
- Thread
- Replies: 25
- Forum: Thermodynamics
-
A
Ball does not bounce automatically because of entropy?
When reading about entropy it states that ball does not automatically bounce up because of entropy. It is just not favorable. I don't get this. Isn't the correct reason gravity? Ball does not bounce up because of gravity! Where does entropy come from?- Avichal
- Thread
- Replies: 10
- Forum: Thermodynamics
-

Can the Entropy of an Isolated System Decrease?
So in my physics textbook, the 2nd law of thermodynamics stated in terms of entropy reads "the entropy of a closed system can never decrease." Now, shouldn't it indicate the entropy of an isolated system can never decrease. All other sources I've looked at note an isolated system, as well...- NATURE.M
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Closed Closed system Entropy System
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Thermodynamics
-
N
Entropy: Increasing or Decreasing?
Everybody says entropy of the universe is increasing. But after the big bang, matter formed, it came together, stars and galaxies were formed, on a small planet called Earth atoms/molecules came together to form unicellular organisms and then higher life. Our brains are organizing even more...- Naveen3456
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Entropy
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Thermodynamics
-
F
Maximum Entropy in Gaussian Setting
Hello, I have a doubt about the distribution of random variables that maximize the differential entropy in a set of inequalities. It is well known that the Normal distribution maximizes the differential entropy. I have the following set of inequalities: T1 < I(V;Y1|U) T2 < I(U;Y2) T3 <...- ferreat
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Set Theory, Logic, Probability, Statistics
-
A
Why is there zero resistivity in superconductors when there is non-zero entropy?
According to theory of superconductivity, resistivity almost zero. Below critical temperature the entropy decreases markedly with cooling . why resistivity zero when entropy not equal to zero? my doubt is when there is an entropy there is a disorder. then how can move conducting electron...- anuraj.b
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Entropy Superconductivity
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Atomic and Condensed Matter
-
B
A Tricky Problem Involving Entropy
So we learn in basic thermo that for any system, the derivative of entropy with respect to volume is pressure over temperature: ∂S/∂V=P/T. Suppose we have a box with two partitions, and a moveable wall in between the partitions. The box and wall are both insulated to prevent heat transfer...- BucketOfFish
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Entropy
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Thermodynamics
-
M
Entropy in Cosmology: Exploring the Universe
So we know that at the moment of the big bang the universe was relatively low in entropy; as the universe has expanded entropy has increased, but what about further down the line? What about when the universe is so cold that it's nothing more than a collection of black holes, and further more...- m_robertson
- Thread
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Cosmology
-
S
Adiabatic expansion, entropy change
Homework Statement 1 mol of monoatomic ideal gas (temperature T1) is inside a cylinder with a moving piston (all are isolated). The initial external pressure on the piston is P1. at some point the external pressure is changed to (2/3)P1, the gas undergoes (irreversible) adiabatic expansion...- susdu
- Thread
- Replies: 12
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-

Significance for LQG of Sen's result on entropy of black holes?
Sen 2013 says, How serious a problem is this for LQG? Does this mean that LQG doesn't have GR as its semiclassical limit? Does that mean it's a dead theory, or maybe just that it needs to be modified? Is the technique using Euclidean gravity reliable? Since I'm not a specialist, I'd be...- bcrowell
- Thread
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Beyond the Standard Models
-
F
Change of entropy - Isothermal
Can someone explain to me why Cpln(T2/T1) = 0? Thank you.- freshbox
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Change Entropy Isothermal
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
D
How Do You Calculate the Change in Entropy When Ice Melts in Water?
In 250gr water at 23 oC(degrees celsius) we throw in 27gr ice at 0 oC. Find the change in entropy. (sorry if that was a bad translation but English is not my native language) The answer is 0.78 calories/oC. But I'm not sure how do this. The formula I have for entropy is: S=δQ/T I find the...- devil0150
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Thermodynamics
-
E
Entropy increase,coarse-grained vs. Landauer's principle justification
First off, just clarify that I have a very, very superficial knowledge of Physics, so my apologies if my question is based on an obvious misunderstanding of the basic principles underlying the second law of thermodynamics or if it has a rather simple answer. The doubt that I have is related...- Evaristo
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Thermodynamics
-

Loop Quantum Gravity and entropy
How specifically does LQG explain how the universe can oscillate from big bang to big crunch ad infinitum? Wouldn't the total energy able to be used as work decrease after a couple of bounces? Am I simply misunderstanding or making a false assumption about what LQG's premises are? I've not...- Digitalism
- Thread
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Beyond the Standard Models
-
L
How Is Entropy Calculated for a Density Matrix with Eigenvalues 0 and 1?
Homework Statement Calculate entropy for density matrix with eigenvalues ##0## and ##1##. Homework Equations ##S=-\lambda_1 \ln \lambda_1-\lambda_2 \ln \lambda_2## where ##\lambda_1## and ##\lambda_2## are eigenvalues of density matrix. The Attempt at a Solution How to calculate...- LagrangeEuler
- Thread
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
V
Relating physics forces and entropy
Consider proton and electron are separated in space at some finite distance.Now suppose they released then the decrease in potential energy equals kinetic energy but as electrons or protons are accelerated they emit em and lose some gained kinetic energy.Also the mass is another form of...- vishvajeet
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Thermodynamics
-
T
Entropy and electromagnetic radiation
I don't understand this: According to what modern physicists believe to be true, there is entropy that slowly converts all energy of the universe into heat that cannot do any work. Than this heat is radiated as infrared light into space. Correct? Besides infrared heat radiation, start also...- tarakan
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
S
Entropy of a rubber-band (force determined by entropy or energy)?
Homework Statement The resultant of a experimental run of a force (N) vs temperature (K) gives me a slope of 0.0039x - 1.0929. The slope has a (∂f/∂T)l = (∂S/∂l)T Homework Equations Equation (11) attached as PNG file We can obtain all the quantities of the right side of Eq. (11)...- sdnnet3
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
S
How meaurements increase entropy?
¿ How meaurements increase entropy? The decoherence before the measurement increase entropy but collapse returns the state of the system to a pure state. ¿Why then measurements increase entropy- StarsRuler
- Thread
- Replies: 9
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
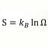
Entropy Of Mixing and Specific Heat
Homework Statement 100g of lead, specific heat .0345 cal/g/C at 100 C is mixed with 200 g of water at 20 C. Find the difference in entropy of system at end from value before mixing. Note: I think the book has wrong answer of 1.42 cal/K Homework Equations Before mixing entropy for water =...- morrobay
- Thread
- Replies: 17
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
G
Will the fusion reactor ITER decrease entropy?
ITER is the fusion reactor in southern France that hopefully will come online in 2018. According to wiki http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ITER The ITER fusion reactor itself has been designed to produce 500 megawatts of output power for 50 megawatts of input power. Does this mean that if...- g.lemaitre
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: High Energy, Nuclear, Particle Physics
-
B
Which has least entropy- living organism or same mass as chrystal?
Which has the least entropy? A 1kg diamond vs 1kg living organism I've gather that living things are generally at a state of low entropy compared to the same matter in other configurations- as though complexity goes hand in hand with low entropy. Yet a perfect chrystal is supposedly low...- bcrelling
- Thread
- Replies: 11
- Forum: Thermodynamics
-
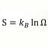
Entropy For Irrevesible Process
Homework Statement Two 100g Aluminum cubes with T1 = 80° C and T2 = 20°C Specific heat of Al is .22 cal/g/°C. The cubes are placed in contact and in short period of time a quantity of heat, dQ , is transferred from T1 cube to T2 cube. The cubes temperatures now are 75°C and 25°C. After a...- morrobay
- Thread
- Replies: 9
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
G
Entropy problem involving saltwater uptake into a cell
Homework Statement For public health reasons, you are investigating small systems that turn sea water into drinking water. One portable system takes a volume of saltwater and produces two thirds that volume of freshwater with an increased concentration of salt in the other third of the volume...- GoGoGadget
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
A
Why is entropy a driving force for a reaction
I understand the Gibbs Free Energy equation that was drilled into us in Chemistry class but not even my teacher could explain what entropy had to do with free energy, and furthermore, why entropy is a driving force for a reaction. From what I understand, entropy is the distribution of energy...- arp001
- Thread
- Replies: 11
- Forum: Thermodynamics