- #1
shell4987
- 43
- 0
Homework Statement
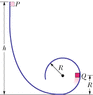
In Fig. 8-33, a small block of mass m = 0.040 kg can slide along the frictionless loop-the-loop, with loop radius R = 14 cm. The block is released from rest at point P, at height h = 9R above the bottom of the loop. How much work does the gravitational force do on the block as the block travels from point P to (a) point Q and (b) the top of the loop? If the gravitational potential energy of the block-Earth system is taken to be zero at the bottom of the loop, what is that potential energy when the block is (c) at point P, (d) at point Q, and (e) at the top of the loop?
**image attached**
Homework Equations
w=mgh
The Attempt at a Solution
I've completed parts (a) through (c) and got those correct, however I cannot get a correct answer for (d) and (e), I used W=mgR and plugged in 0.040(9.8)(0.14)= 0.05488 mJ for (d) and then I used W=mg2R for (e) with plugging in 0.040(9.8)(2)(0.14)= 0.10976mJ... I need to convert these into joules and I did so and still got the wrong answer, I just want to know if I'm doing something wrong with the physics part of the problems?