- #1
oksuz_
- 70
- 3
Hi,
Below are the neutron flux spectra of a nuclear reactor. In the first spectrum, y-axis is differential flux and in the second spectrum, y-axis is flux (created by multiplying differential flux by energy in MeV). As far as I have seen so far, differential flux is used commonly. I am just wondering that why it is like that. Is there an advantage for using differential flux instead of just flux?
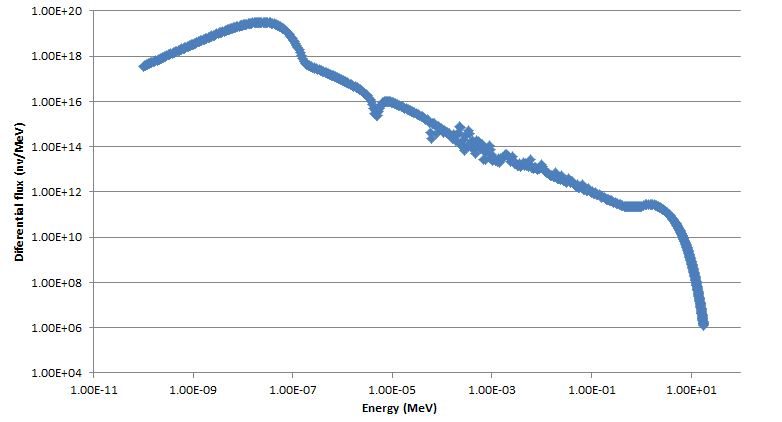
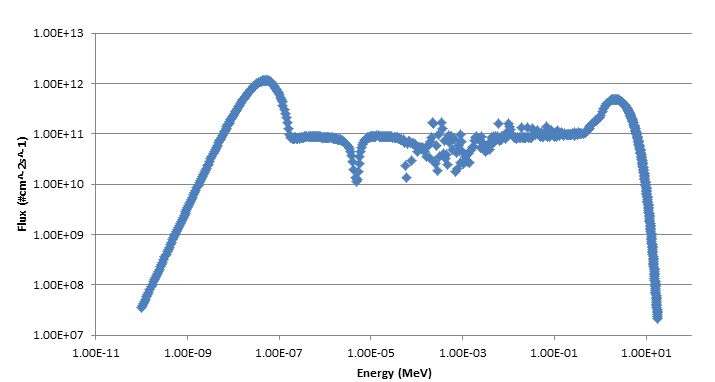
Thank you.
Below are the neutron flux spectra of a nuclear reactor. In the first spectrum, y-axis is differential flux and in the second spectrum, y-axis is flux (created by multiplying differential flux by energy in MeV). As far as I have seen so far, differential flux is used commonly. I am just wondering that why it is like that. Is there an advantage for using differential flux instead of just flux?
Thank you.

