- #1
JessEE92
- 1
- 0
According to this article, it is beneficial to scale down heat exchangers due to the decreased distance the heat has to travel, and therefore the decreased thermal resistance and increased heat flow.
"the best way to remove heat from a CPU is to minimize the distance heat must travel from a CPU's hotspot to the heat collector before it's carried away"
However what confuses me is that their are more things that affect heat flow than travel distance, and to me it seems that scaling down the heat exchanger to micro and nano scales would be detrimental to performance. For example the heat capacitance of the exchanger will go down with its reduced mass, therefore it will get to much hotter temperatures while removing smaller amounts of energy. The thermal conductance of silicon decreases for hotter temperatures so this will decrease heat flow.
It all depends on how the properties scale. Will the advantage of decreased travel distance outweigh the disadvantage of lower heat capacity as you scale down?
My second question is: Are there other relevant properties (thermal or otherwise) that are effected by scaling heat exchangers?
Here is a diagram of the heat exchanger in question:
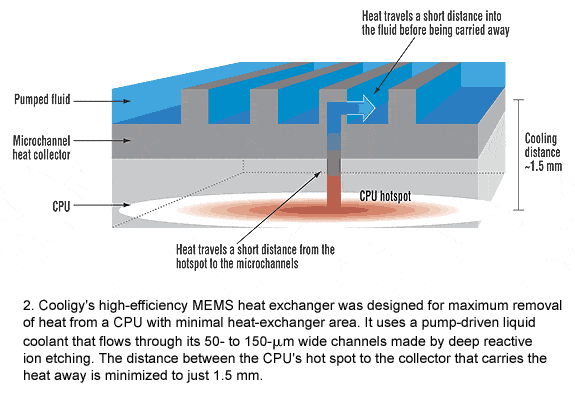
"the best way to remove heat from a CPU is to minimize the distance heat must travel from a CPU's hotspot to the heat collector before it's carried away"
However what confuses me is that their are more things that affect heat flow than travel distance, and to me it seems that scaling down the heat exchanger to micro and nano scales would be detrimental to performance. For example the heat capacitance of the exchanger will go down with its reduced mass, therefore it will get to much hotter temperatures while removing smaller amounts of energy. The thermal conductance of silicon decreases for hotter temperatures so this will decrease heat flow.
It all depends on how the properties scale. Will the advantage of decreased travel distance outweigh the disadvantage of lower heat capacity as you scale down?
My second question is: Are there other relevant properties (thermal or otherwise) that are effected by scaling heat exchangers?
Here is a diagram of the heat exchanger in question: