- #1
mindboggling
- 16
- 0
I'm looking for something that can pull on a string at a constant force per second
So that i can graph Force (n) over Time (s) just like that:
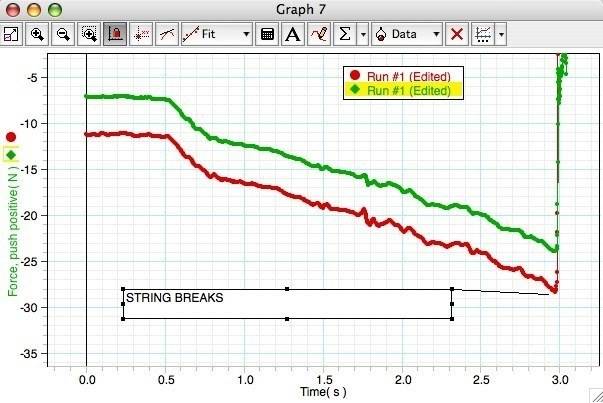
in this graph, the red line represents the tension of a string as i pull on it. However, i really need that slope to be constant.
By the I'm investigating how different force per second affects the breaking force of the string
From preliminary experiments, i observed that that:
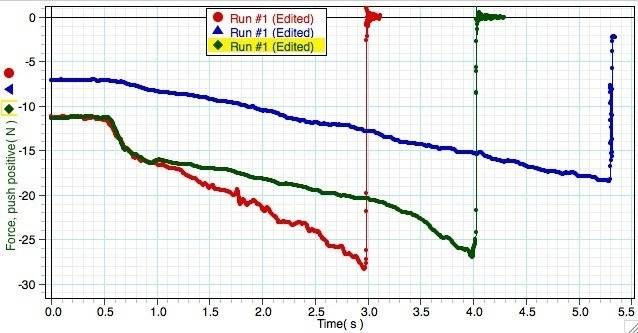
the trough of the graph is when the string breaks.
The larger N/s applied, the string breaks at a higher tension
The lower N/s applied, the string breaks at a lower tension
WHY IS THIS SO? which equations can i use?
So that i can graph Force (n) over Time (s) just like that:
in this graph, the red line represents the tension of a string as i pull on it. However, i really need that slope to be constant.
By the I'm investigating how different force per second affects the breaking force of the string
From preliminary experiments, i observed that that:
the trough of the graph is when the string breaks.
The larger N/s applied, the string breaks at a higher tension
The lower N/s applied, the string breaks at a lower tension
WHY IS THIS SO? which equations can i use?
Last edited: