- #1
Raudi
- 1
- 0
Hi
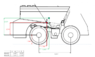
I am trying to compare which of the (2) models has the greatest stability longitudinaly.
I have the COG height and longitudinal (axle split)
Model A has it COG closer to the centre of the axles (longitudinal - further from rear axle 1,487l) but sits much higher (2,537 above axle centre)
Model B has its COG closer to the rear axle (1,141) but sits much lower (1,745mm from axle centre)
Obviously there is a trade off going higher with the COG.
I believe that Model B has the greater all round stability by around 9%
The main factor that is trying to be quantified is which model is more likely to tip backwards.
X → Y ↑
Model A 1,487 2,537
Model B 1,141 1,745
I am trying to compare which of the (2) models has the greatest stability longitudinaly.
I have the COG height and longitudinal (axle split)
Model A has it COG closer to the centre of the axles (longitudinal - further from rear axle 1,487l) but sits much higher (2,537 above axle centre)
Model B has its COG closer to the rear axle (1,141) but sits much lower (1,745mm from axle centre)
Obviously there is a trade off going higher with the COG.
I believe that Model B has the greater all round stability by around 9%
The main factor that is trying to be quantified is which model is more likely to tip backwards.
X → Y ↑
Model A 1,487 2,537
Model B 1,141 1,745