- #1
baby_1
- 159
- 15
Moved from another forum, so homework template missing
Hello
In this problem I tried to find the voltage at 2Z0 (load) that is (landa/4) from generator.My result it is different from teacher's result.what is my mistake?
(I named V1e as A point and V2e as B point so the voltage across the B point is (Vs/4) according to Zin=Z0 that is the same as Z0 of generator's impedance)
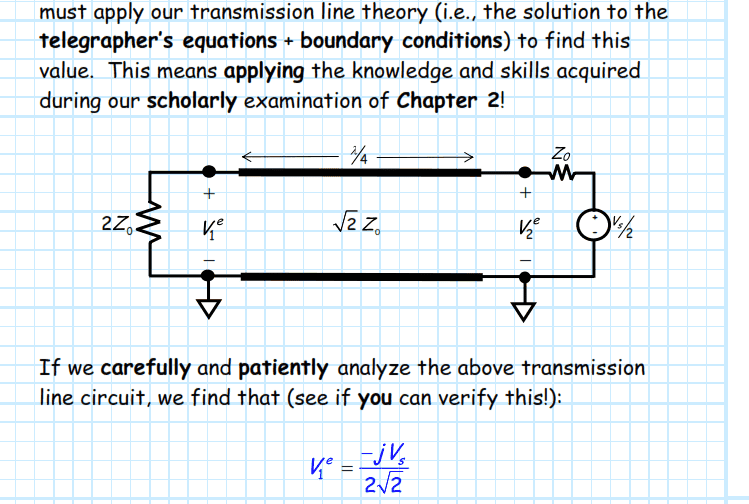
my solution:

Any helo would appreciate
In this problem I tried to find the voltage at 2Z0 (load) that is (landa/4) from generator.My result it is different from teacher's result.what is my mistake?
(I named V1e as A point and V2e as B point so the voltage across the B point is (Vs/4) according to Zin=Z0 that is the same as Z0 of generator's impedance)
my solution:
Any helo would appreciate