- #1
Pinon1977
- 126
- 4
- TL;DR Summary
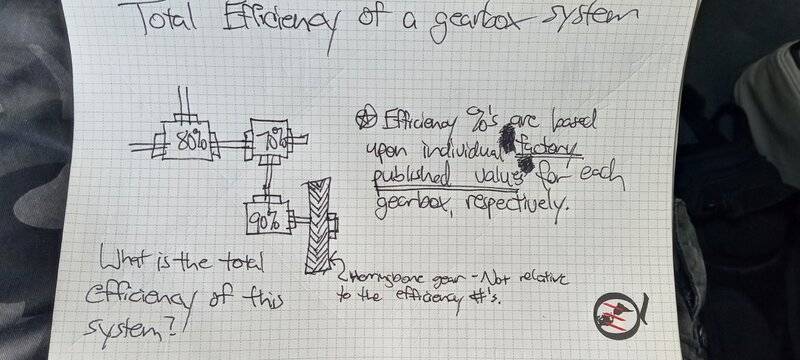
- Trying to determine the total efficiency of a system of gearboxes within a larger machine system
Please see the attached sketch. Basically I have a system of three gear boxes, each with their own respective efficiencies. I'm trying to determine, at the end of this string of gearboxes, what the overall efficiency is. How might one go about determining this? Do you just take the average? 70 + 80 + 90 / 3?