- #1
Exploded_Muffin
- 1
- 0
Can someone please help me with the following proof ...I'm stuck and not sure if I'm even on the right path.
Prove that
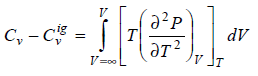 What I've done so far;
What I've done so far;
if U = f(T,V)
dU = (∂U/∂T)v dT + (∂U/∂V)t dV
Cv (non ideal) = (∂U/∂T)v
Using dU = TdS - PdV and Maxwell relation (∂S/∂V)t =(∂P/∂T)v,
(∂U/∂V)t = T(∂P/∂T)v - P
So;
dU = CvdT + [ T(∂P/∂T)v - P ]dv
I'm basically stuck here, tried different ways forward from here but I can't seem to arrive at the correct answer. Any help would be
Prove that
if U = f(T,V)
dU = (∂U/∂T)v dT + (∂U/∂V)t dV
Cv (non ideal) = (∂U/∂T)v
Using dU = TdS - PdV and Maxwell relation (∂S/∂V)t =(∂P/∂T)v,
(∂U/∂V)t = T(∂P/∂T)v - P
So;
dU = CvdT + [ T(∂P/∂T)v - P ]dv
I'm basically stuck here, tried different ways forward from here but I can't seem to arrive at the correct answer. Any help would be