- #1
Urmi Roy
- 753
- 1
Referring to first figure attached, if we put a system of a certain composition at a T and P corresponding to a point inside the spinodal, will it (with very small fluctuations) just jump to the corresponding binodal compositions at that temperature and pressure? As per this figure, the system would assume compositions that we could tell by drawing a horizontal line and seeing which values of x of each component takes.
However on the phase diagrams for, say, water (ref 2nd figure) if we put a system in the spinodal region, it becomes either liquid or gas... what exactly is the difference between the above two cases?
Another thing I was wondering about, is that a system while moving away from the spinodal region need not necessarily move to the binodal composition..isn't it possible for it to just sit in a metastable state or on the spinodal curve itself?
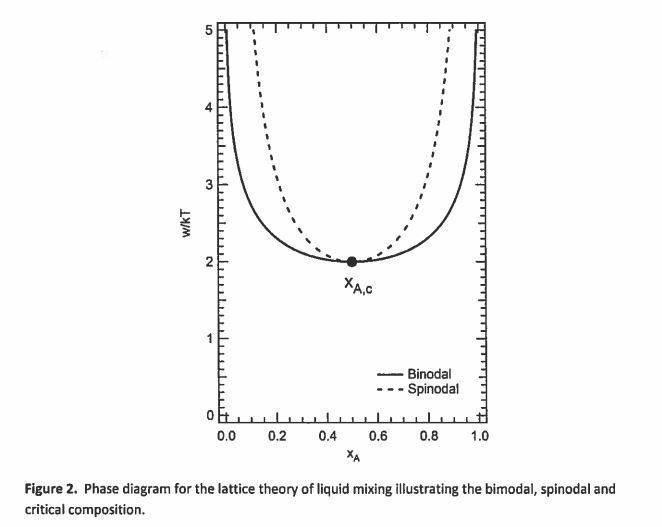

However on the phase diagrams for, say, water (ref 2nd figure) if we put a system in the spinodal region, it becomes either liquid or gas... what exactly is the difference between the above two cases?
Another thing I was wondering about, is that a system while moving away from the spinodal region need not necessarily move to the binodal composition..isn't it possible for it to just sit in a metastable state or on the spinodal curve itself?