- #1
usn7564
- 63
- 0
Homework Statement
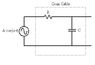
Signals from sources of different kinds are often very weak and very quick. To minimize the noise risk they're often led through coaxial cables. How long can one [coaxial cable] be if it has the capacitance 80pF / m and resistance 0.04 Ohm/m and you want to transfer noise that varies on 100 nano seconds?
Homework Equations
time constant = RC
The Attempt at a Solution
Right, so have the solution which basically just outlines what you do. You find the length L so that t is less or equal to RC. The cable is regarded as an RC circuit.
But I don't get the physics at all, what am I actually looking for? Noise that varies on 100 ns? (It's a direct translation but I honestly don't understand it better in my native tongue). What's special about t < RC in this scenario?