- #1
alikazemi7
- 8
- 0
Hi
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mathematical_descriptions_of_opacity
it is mentioned above that "in non attenuating media, the refractive index and angular wavenumber are related by:
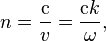
A complex refractive index can therefore be defined in terms of the complex angular wavenumber defined above:
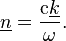
where n is the refractive index of the medium."
Is it right to say that some mediums are attenuating and some non attenuating? and we use
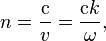 for non attenuating mediums and
for non attenuating mediums and
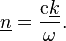 for attenuating mediums?
for attenuating mediums?
or non attenuating situations is just an approximation and all media are attenuating?
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mathematical_descriptions_of_opacity
it is mentioned above that "in non attenuating media, the refractive index and angular wavenumber are related by:
A complex refractive index can therefore be defined in terms of the complex angular wavenumber defined above:
where n is the refractive index of the medium."
Is it right to say that some mediums are attenuating and some non attenuating? and we use
or non attenuating situations is just an approximation and all media are attenuating?