- #1
RingNebula57
- 56
- 2
Is it possible that 2 stars in a binary system to intersect their orbits like in this picture? ( the orbital plane is perpendicular to the line of sight)
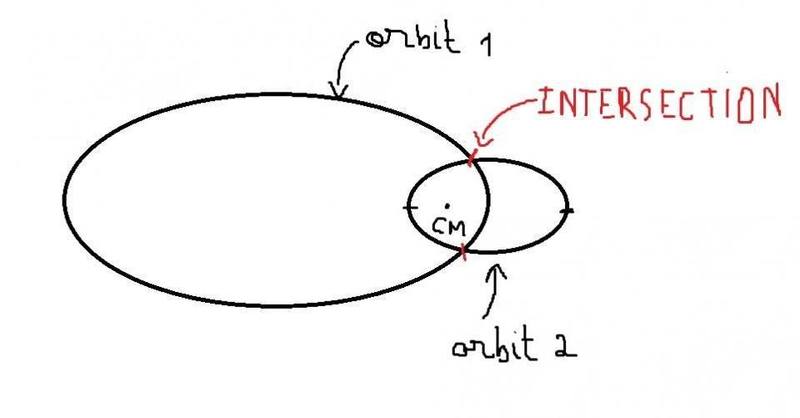
why?mathman said:Since they are revolving around their center of mass, the orbits will intersect as long as the stars are similar in size.
The orbits are coplanar, as they have to be in a 2-body interaction. As long as you can treat both bodies as point masses, the only condition for intersection is that the periapsis of the less massive body is closer to the centre of mass than the apoapsis of the more massive one. This depends on the combination of the ratio of masses and eccentricity.RingNebula57 said:why?
thank you! I got ittony873004 said:http://orbitsimulator.com/gravitySimulatorCloud/simulations/binary.html
Here's a simulation of this happening.
Intersecting orbits of binary stars refer to the paths of two stars that are gravitationally bound to each other and orbit around a common center of mass. These orbits intersect each other, meaning that at certain points, the stars will appear to cross paths as seen from Earth.
Intersecting orbits of binary stars are formed when two stars are formed close together in a molecular cloud, and their gravitational pull causes them to orbit around each other. This can also occur when two stars are captured by each other's gravity after forming separately.
Studying intersecting orbits of binary stars can provide valuable insights into the formation and evolution of binary star systems. It can also help us better understand the dynamics of gravitational interactions between celestial bodies.
Intersecting orbits of binary stars can be observed through various methods, including spectroscopy, which measures the light emitted by the stars to determine their orbital velocity and distance from each other. Astrometry, which tracks the positions of the stars over time, can also be used to observe intersecting orbits.
Yes, intersecting orbits of binary stars can be stable if the stars have a relatively equal mass and the orbits are circular. However, if there is a significant difference in mass or the orbits are highly elliptical, the system may become unstable and eventually result in a merger or ejection of one of the stars.