- #1
vtaela
- 25
- 0
i am looking for the amplitude ratio and phase shift of this graph? could someone explain me how to obtain these results from this type of graph?
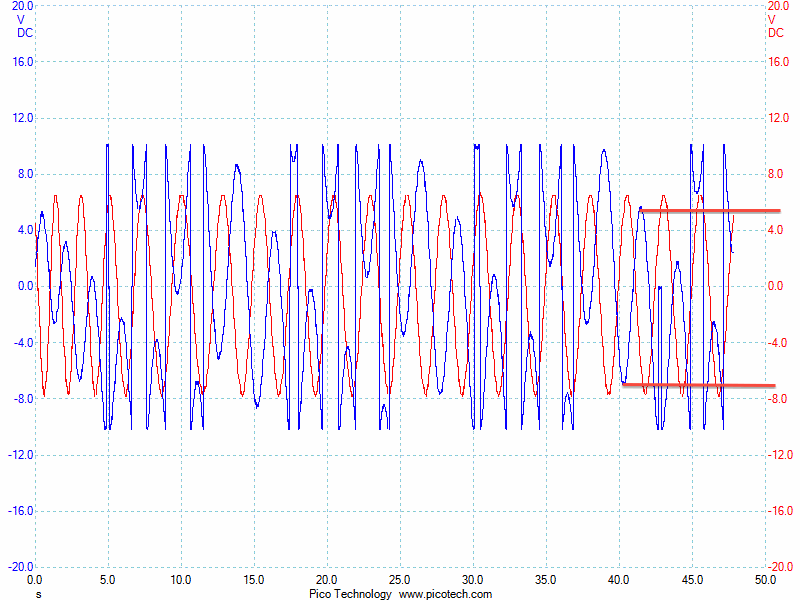
thank you
thank you
The phase shift in a wave refers to the horizontal displacement of the wave from its original position. It can be measured in degrees or radians and is typically denoted by the symbol phi (φ). To find the phase shift, you need to compare the starting point of the wave with the current point of the wave, and the difference between the two represents the phase shift.
The amplitude ratio of a wave is the ratio of the amplitude of the output wave to the amplitude of the input wave. To calculate this ratio, you need to measure the amplitude of both waves and then divide the amplitude of the output wave by the amplitude of the input wave. The resulting value will be the amplitude ratio.
The phase shift and amplitude ratio are both measures of how a wave changes over time. They are not directly related to each other, but they can both be used to describe the characteristics of a wave. In general, an increase in the phase shift will result in a decrease in the amplitude ratio, and vice versa.
To find the phase shift and amplitude ratio of a sound wave, you need to first record the sound and visualize it on a graph. The phase shift can be determined by comparing the starting point of the wave with the current point of the wave. The amplitude ratio can be calculated by measuring the amplitude of the sound wave at different points and then dividing the amplitude of the output wave by the amplitude of the input wave.
Some common methods for finding the phase shift and amplitude ratio of a wave include using a graph to visually compare the starting point and current point of the wave, using trigonometric functions such as sine and cosine to calculate the phase shift, and using measuring tools to determine the amplitude of the wave at different points. Computer software programs can also be used to analyze and calculate these values accurately.