- #1
trevo100
- 1
- 0
Homework Statement
Consider two blocks connected by a light, inextensible string over a light pulley
as follows:
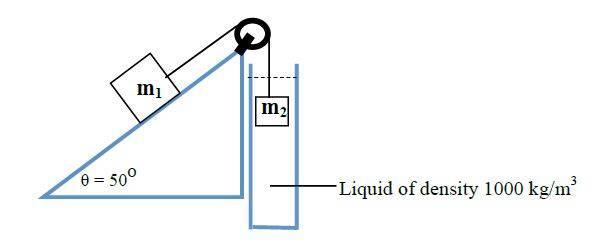
The slope is frictionless and the masses are released from rest. The mass m1 is
3 kg and the mass m2 is 4 kg where m2 is submerged completely (from the
beginning) in a liquid of density 1000 kg/m3. Take the density of m2 to be
8000kg/m3 and the drag force (in Newtons) to be FD = 7v, find the terminal
velocity of m2. (Hint: Don’t forget to include upthrust.)
The attempt at a solution
m1*g*sin50 + Fupthrust - fdrag - m2*g = (m1+m2)*a, when it reaches terminal velocity, acceleration becomes 0
22.5 + 4.9 - 39.2 -Fdrag = 0
Fdrag = -11.8
7v = -11.8
v = -1.68 m/s
The solution from my prof is 1.68m/s, but I can't figure out why I got minus in the equation.
Consider two blocks connected by a light, inextensible string over a light pulley
as follows:
The slope is frictionless and the masses are released from rest. The mass m1 is
3 kg and the mass m2 is 4 kg where m2 is submerged completely (from the
beginning) in a liquid of density 1000 kg/m3. Take the density of m2 to be
8000kg/m3 and the drag force (in Newtons) to be FD = 7v, find the terminal
velocity of m2. (Hint: Don’t forget to include upthrust.)
The attempt at a solution
m1*g*sin50 + Fupthrust - fdrag - m2*g = (m1+m2)*a, when it reaches terminal velocity, acceleration becomes 0
22.5 + 4.9 - 39.2 -Fdrag = 0
Fdrag = -11.8
7v = -11.8
v = -1.68 m/s
The solution from my prof is 1.68m/s, but I can't figure out why I got minus in the equation.