- #1
piareround
- 79
- 0
Dear Sir and Mam,
So recently, I have been doing an experiment with Faraday waves. I feel like there are some critical things I don't understand about fluid dynamics (they don't offer it as a course where I go to school), so I was wondering if anyone on pf was good with fluid dynamics and help me understand the qualitative side of Faraday Waves.
In the experiment we vertically shake water with speaker-like device. At certain critical amplitude and frequency, we observe Faraday waves like in Fig. 1 below.
On of the things that really mystify's me is difference the growth of Faraday waves vs. the decay of Faraday waves. For example, let say I introduce a constant sinusodial variation to the speaker. If I plot the acceleration of the speaker vs. the magnitude out put of the Faraday wave, I get something like Fig. 2. Here it easy to see how the onset of the Faraday is quiet sudden vs. the long decrease in Faraday waves.
Can anyone explain qualitatively how or why an oscillation grow differently than its decay?
I have heard some paper use the word "primary Faraday instability". Could it have anything to do with an instability?
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=<iframe width="420" height="315" src="http://www.youtube.com/embed/v-XEhY4OThs" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen></iframe>
Fig. 1: The following youtube video is
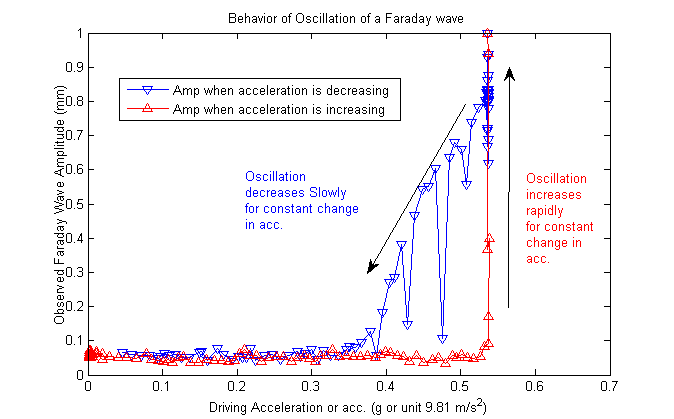
Fig 2: A picture of the Amplitude vs. acceleration graph. It shows how the growth and decay behavior of a Faraday Wave are different.
So recently, I have been doing an experiment with Faraday waves. I feel like there are some critical things I don't understand about fluid dynamics (they don't offer it as a course where I go to school), so I was wondering if anyone on pf was good with fluid dynamics and help me understand the qualitative side of Faraday Waves.
In the experiment we vertically shake water with speaker-like device. At certain critical amplitude and frequency, we observe Faraday waves like in Fig. 1 below.
On of the things that really mystify's me is difference the growth of Faraday waves vs. the decay of Faraday waves. For example, let say I introduce a constant sinusodial variation to the speaker. If I plot the acceleration of the speaker vs. the magnitude out put of the Faraday wave, I get something like Fig. 2. Here it easy to see how the onset of the Faraday is quiet sudden vs. the long decrease in Faraday waves.
Can anyone explain qualitatively how or why an oscillation grow differently than its decay?
I have heard some paper use the word "primary Faraday instability". Could it have anything to do with an instability?
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=<iframe width="420" height="315" src="http://www.youtube.com/embed/v-XEhY4OThs" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen></iframe>
Fig. 1: The following youtube video is
Fig 2: A picture of the Amplitude vs. acceleration graph. It shows how the growth and decay behavior of a Faraday Wave are different.