- #1
cupid.callin
- 1,132
- 1
Hi all
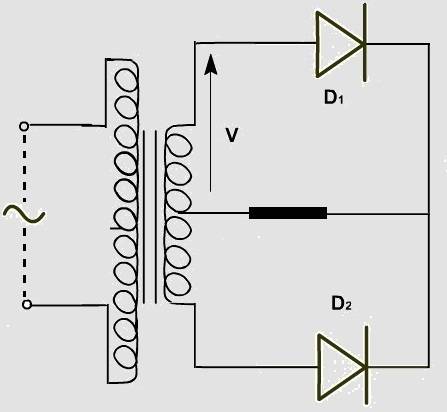
So my question is, ...
suppose we apply sine wave at the 2 ends, th the cycle [itex]0 \rightarrow \pi[/itex] will all the coils of secondary coil of transformer be used or just upper half of it (assuming currently upper side is getting positive polarity) ...
I think only half should be used ...
Any help?
So my question is, ...
suppose we apply sine wave at the 2 ends, th the cycle [itex]0 \rightarrow \pi[/itex] will all the coils of secondary coil of transformer be used or just upper half of it (assuming currently upper side is getting positive polarity) ...
I think only half should be used ...
Any help?
