- #1
PCarson85
- 3
- 1
If I have a motor that is turning a shaft with only a small torque required but the shaft is also being forced into the motor, axially at a large force, what is the effect on the motor here?
If Faxial is large, does this effect T and how does this effect the motor?
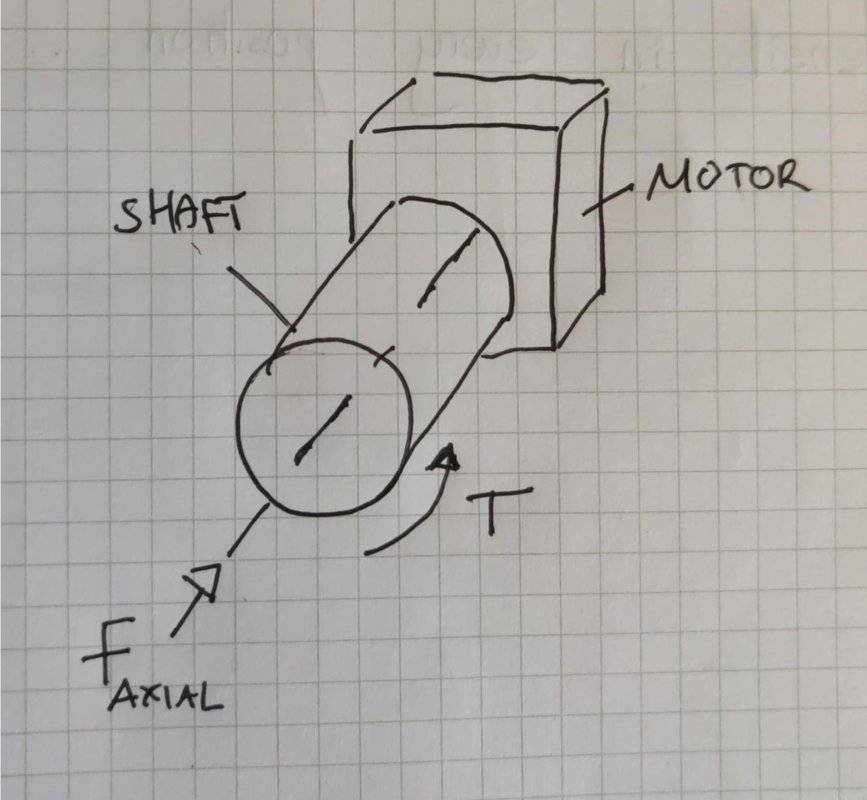
If Faxial is large, does this effect T and how does this effect the motor?