- #1
Sven Andersson
- 38
- 0
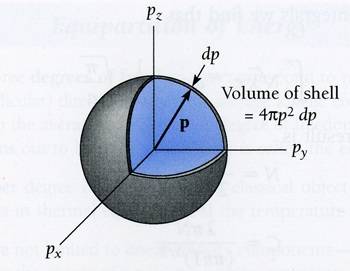
How are protons in an ion source distributed in momentum space? Consider an ion source fed with H2 at low pressure. As soon as the protons are free protons they are accelerated by the extraction voltage of perhaps 10 kV. In momentum space the protons are initially a "shell" with a certain diameter and thickness, like in the picture below. Let's say that the extraction is along the y-axis, so to speak. Then that "shell" moves to the right in the picture as the protons are accelerated. But continously new shells should emerge at the origin as H2 is ionized. And collisions will also create new populations (larger shells?) in momentum space. How can a complete description be formed of this?