- #1
wmsaqqa
- 28
- 0
What is the prove for this formula, or in another way the provement of the dynamic viscosity multiplied by the shear strain will get us the shear stress,
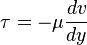
wmsaqqa said:What is the prove for this formula, or in another way the provement of the dynamic viscosity multiplied by the shear strain will get us the shear stress,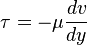
Fluid mechanics is a branch of physics that studies the behavior of fluids (liquids and gases) at rest and in motion. It involves the study of properties such as pressure, velocity, and viscosity of fluids, and how they interact with their surroundings.
Fluid mechanics has many practical applications in our daily lives, including the design of pumps, turbines, and engines for transportation, the study of air and water currents for weather forecasting, and the development of medical devices such as ventilators and blood flow monitors.
Fluid mechanics is closely related to other branches of physics, such as thermodynamics, electromagnetism, and acoustics. It also has applications in engineering fields such as aerospace, mechanical, and chemical engineering.
Some key principles of fluid mechanics include the conservation of mass, momentum, and energy, as well as the equations of motion (such as Bernoulli's principle) that describe how fluids behave under different conditions.
Fluid mechanics plays a crucial role in the study of natural phenomena such as ocean currents, atmospheric dynamics, and the movement of pollutants in air and water. It helps us understand and predict the impact of human activities on the environment and how to mitigate them.