- #1
Brown Arrow
- 101
- 0
Circular Diffraction Patterns HELP!
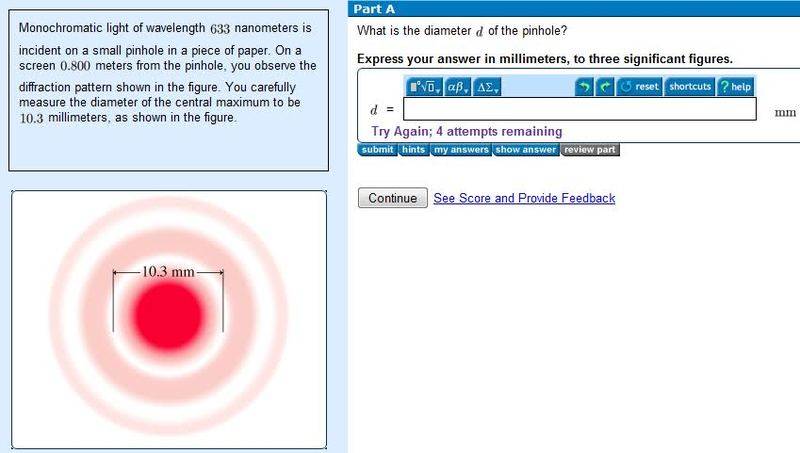
theata_1=1.22(lambda)(L)/D L distance from screen, D diameter of slit
w=2.44(lambda)(L)/D
so this is what i did not sure where i went wrong maybe at rounding off...
w=2.44(lambda)(L)/D
(10.3/1000)=92.44)(633*10^(-9))(0.8)/D
solving for D i got the diameter to be the following
D=0.119962...mm
i rounded off to three significant figure
D=0.120mm is this correct b/c when i did this i got it wrong, could some one tell me where i went wrong this.
Homework Statement
Homework Equations
theata_1=1.22(lambda)(L)/D L distance from screen, D diameter of slit
w=2.44(lambda)(L)/D
The Attempt at a Solution
so this is what i did not sure where i went wrong maybe at rounding off...
w=2.44(lambda)(L)/D
(10.3/1000)=92.44)(633*10^(-9))(0.8)/D
solving for D i got the diameter to be the following
D=0.119962...mm
i rounded off to three significant figure
D=0.120mm is this correct b/c when i did this i got it wrong, could some one tell me where i went wrong this.
Last edited: