- #1
Lindsayyyy
- 219
- 0
Hi everyone
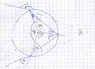
Let's say we observe a rainbow. We know the refraction index of the red and violet light, let's call them [tex] n_{1}=1.46 [/tex]and [tex]n_{2}1.47[/tex] Now I want to calculate the angle [tex] \delta [/tex]
In a square the total angle is 360°, so we have:
[tex] 360°= \delta+\alpha+\alpha+(360°-4\beta)[/tex]
and
[tex]\delta= 4\beta-2\alpha=4arcsin(\frac {1} {n} sin\alpha)-2\alpha [/tex]
Thats my attempt thus far, which I wrote down in the relevant equations. I have two unkown variables, alpha and delta and I want to calculate alpha. Is there a way to calculate alpha in order to get delta?
Thanks for your help
Homework Statement
Let's say we observe a rainbow. We know the refraction index of the red and violet light, let's call them [tex] n_{1}=1.46 [/tex]and [tex]n_{2}1.47[/tex] Now I want to calculate the angle [tex] \delta [/tex]
Homework Equations
In a square the total angle is 360°, so we have:
[tex] 360°= \delta+\alpha+\alpha+(360°-4\beta)[/tex]
and
[tex]\delta= 4\beta-2\alpha=4arcsin(\frac {1} {n} sin\alpha)-2\alpha [/tex]
The Attempt at a Solution
Thats my attempt thus far, which I wrote down in the relevant equations. I have two unkown variables, alpha and delta and I want to calculate alpha. Is there a way to calculate alpha in order to get delta?
Thanks for your help