- #1
Jufa
- 101
- 15
- TL;DR Summary
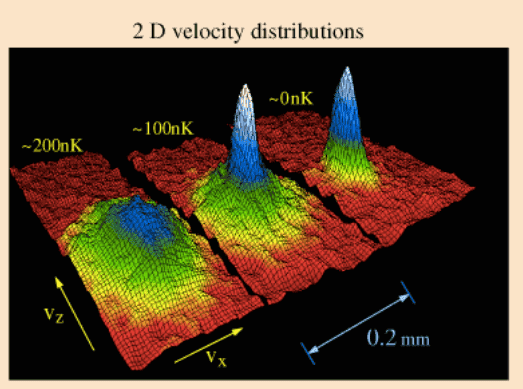
- Struggling with Bose-Einstein condensates diagram.
I have seen many of these diagrams in internet and I fail to figure out what their actual meaning is. Can someone explain what the axes and different colours mean? Also, which is the physical interpretation that can be extracted from them? Thanks in advance :).