- #1
patric44
- 296
- 39
- Homework Statement
- i had an assignment of deriving the Vdc in a fullwave rectifier with smoothing capacitor
- Relevant Equations
- Vdc = V average of the discharging part
i was trying to derive the Vdc in a fullwave rectifier with smoothing capacitor , i guess i had it right as my final equation matches the book equation :
Vdc~(1-(1/2fRC))Vp , but i am not really sure that my attempt was completely right as i assumed that Vdc is the average value of the discharging function neglecting the charging part , and i had to take the first 3 terms of the Taylor approximation to get the answer ,
i just want some one to verify my attempt :
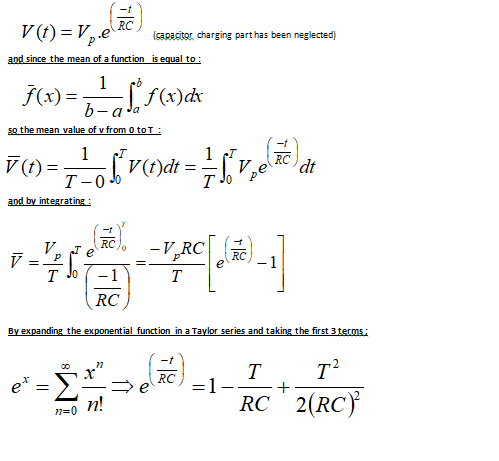
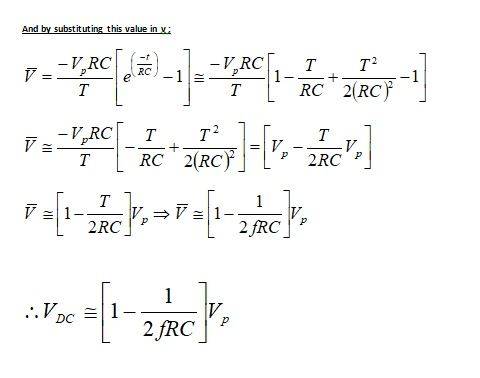
Vdc~(1-(1/2fRC))Vp , but i am not really sure that my attempt was completely right as i assumed that Vdc is the average value of the discharging function neglecting the charging part , and i had to take the first 3 terms of the Taylor approximation to get the answer ,
i just want some one to verify my attempt :