You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
What is Classical mechanics: Definition and 1000 Discussions
Classical mechanics is a physical theory describing the motion of macroscopic objects, from projectiles to parts of machinery, and astronomical objects, such as spacecraft, planets, stars, and galaxies. For objects governed by classical mechanics, if the present state is known, it is possible to predict how it will move in the future (determinism), and how it has moved in the past (reversibility).
The earliest development of classical mechanics is often referred to as Newtonian mechanics. It consists of the physical concepts based on foundational works of Sir Isaac Newton, and the mathematical methods invented by Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz, Joseph-Louis Lagrange, Leonhard Euler, and other contemporaries, in the 17th century to describe the motion of bodies under the influence of a system of forces. Later, more abstract methods were developed, leading to the reformulations of classical mechanics known as Lagrangian mechanics and Hamiltonian mechanics. These advances, made predominantly in the 18th and 19th centuries, extend substantially beyond earlier works, particularly through their use of analytical mechanics. They are, with some modification, also used in all areas of modern physics.
Classical mechanics provides extremely accurate results when studying large objects that are not extremely massive and speeds not approaching the speed of light. When the objects being examined have about the size of an atom diameter, it becomes necessary to introduce the other major sub-field of mechanics: quantum mechanics. To describe velocities that are not small compared to the speed of light, special relativity is needed. In cases where objects become extremely massive, general relativity becomes applicable. However, a number of modern sources do include relativistic mechanics in classical physics, which in their view represents classical mechanics in its most developed and accurate form.
View More On Wikipedia.org
The earliest development of classical mechanics is often referred to as Newtonian mechanics. It consists of the physical concepts based on foundational works of Sir Isaac Newton, and the mathematical methods invented by Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz, Joseph-Louis Lagrange, Leonhard Euler, and other contemporaries, in the 17th century to describe the motion of bodies under the influence of a system of forces. Later, more abstract methods were developed, leading to the reformulations of classical mechanics known as Lagrangian mechanics and Hamiltonian mechanics. These advances, made predominantly in the 18th and 19th centuries, extend substantially beyond earlier works, particularly through their use of analytical mechanics. They are, with some modification, also used in all areas of modern physics.
Classical mechanics provides extremely accurate results when studying large objects that are not extremely massive and speeds not approaching the speed of light. When the objects being examined have about the size of an atom diameter, it becomes necessary to introduce the other major sub-field of mechanics: quantum mechanics. To describe velocities that are not small compared to the speed of light, special relativity is needed. In cases where objects become extremely massive, general relativity becomes applicable. However, a number of modern sources do include relativistic mechanics in classical physics, which in their view represents classical mechanics in its most developed and accurate form.
View More On Wikipedia.org
-

When will the particles collide?
I am stuck. Please ignore my handwriting. I am working on latex. All I am taking is x and y coordinates same of both particles. Yes they will meet at some time t.- rudransh verma
- Thread
- Replies: 18
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

A particle motion problem in the x-y plane with constant acceleration
I have attempted but I don’t get anywhere.- rudransh verma
- Thread
- Replies: 36
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

What kind of motion is this? (bicycle velocity vectors)
How the heck the bicycle reach from point A to point B with that velocity vector directions?- rudransh verma
- Thread
- Replies: 12
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Car traffic producing shock wave
I don’t get where exactly the lengths start and end in figure.- rudransh verma
- Thread
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
I Classical Mechanics - Motion of a particle
Show that a point with acceleration given by: a=c*((dr/dt)×r)/|r|3 where c is a constant, moves on the surface of a cone. This is jut an example to illustrate my doubt. I don't know how to obtain the tracjectory given only the acceleration in this format. I realized that if i can show that...- Einstenio
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Classical Physics
-

B A Question about a Quote from the Feynman lectures
“incidentally, to a good approximation we have another law, which says that the change in distance of a moving point is the velocity times the time interval, Deltas=vdeltat This statement is true only iF the Velocity is not changing during that time interval, and this condition is true only in...- rudransh verma
- Thread
- Replies: 20
- Forum: Mechanics
-

Classical What Are Some General Physics Books to Complement Resnick and Halliday?
I am currently reading some introductory physics. I am following resnik and Halliday. Can anyone suggest me some good general books on physics which would go comfortably with my resnik book. I need to read some general material not something technical. If possible on classical mechanics and...- rudransh verma
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Science and Math Textbooks
-

Trip from San Antonio to Houston
How do you approach the problem as if you have never done it before?- rudransh verma
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

A scooterist trying to overtake truck
If 150s is the time in which overtaking has to occur then why are they using this eqn: xp=x0+xs.- rudransh verma
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Classical mechanics Truck
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Comparing 1000m Race Velocities: Runner 1 vs Runner 2
First I calculated the avg velocity with 1000m for both runners. It came 6.76m/s and 6.75m/s. It suggests that the velocities are same. This means yes that the L2 track is slightly longer than L1. Then why is it asking this question (…that runner 1 is faster)? Both are at equal speeds. I don’t...- rudransh verma
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Classical mechanics Race
- Replies: 31
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Pigeon Problem Solved: Calculating Car Velocities and Meeting Time
The solution was done adding the two velocities of the car while finding the total time it took for the two cars to meet. I don’t really get the solution.- rudransh verma
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Classical mechanics
- Replies: 16
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Intro Physics Exploring Potential Errors in Feynman Lectures on Physics: A Scientific Inquiry
I was reading Motion chapter 8 in Vol 1 and I came across a line in speed topic which seemed confusing. So I checked with others and we concluded that its a mistake. Are there printing mistakes in this book? I will be surprised. Its pearson.- rudransh verma
- Thread
- Replies: 21
- Forum: Science and Math Textbooks
-
K
A When is Hamilton's principle valid?
When is Hamilton's principle##\delta \int L d t=0## valid ? Is it only valid for monogenic and holonomic systems? What about monogenic and non holonomic systems? (I'm asking this because I got confused because I've found that Goldstein has got something wrong related to this in his 3rd edition) -

What is the speed of the bicycle?
- brochesspro
- Thread
- Replies: 57
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
K
A Two equations of generalized forces
Wikipedia article under generalized forces says Also we know that the generalized forces are defined as How can I derive the first equation from the second for a monogenic system ? -
R
Calculate quality factor of a damped oscillation from a graph
I'm trying to find the quality factor of a damped system. I know 3 points from the graph, ##(t,x): (\frac{\pi}{120},0.5), (\frac{\pi}{80},0), (\frac{\pi}{16},0)## From this I found that ##T = \frac{\pi}{20}## ##\omega_d = \frac{2\pi}{T} = 40 rad## Then, from the solution ##x(t) = A_0...- Redwaves
- Thread
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
K
A Hamilton's principle and virtual work by constraint forces
Found a question on another website, I have the exact same question. Please help me Goldstein says : I do not understand how (2.34) shows that the virtual work done by forces of constraint is zero. How does the fact that "the same Hamilton's principle holds for both holonomic and... -
K
A Non holonomic constraints in classical mechanics textbook
I want to learn about the non holonomic case in lagrangian and Hamiltonian mechanics. I've seen that many people say that Goldstein 3rd ed is wrong there. Where should I go to learn it. My mathematics level is at the level Goldstein uses. Please help- Kashmir
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Classical Physics
-
T
Exponential potential energy state diagram
It is my second "energy state diagram problem" and I would want to know if I am thinking correctly. First I have done some function analysis to get a glimpse of the plot: - no roots but ##\lim\limits_{x\to-\infty}U(x)=\lim\limits_{x\to+\infty}U(x)=0## - y interception: ##U(0)=-U_0## - even...- ThEmptyTree
- Thread
- Replies: 13
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
K
I Virtual displacement is not consistent with constraints
Goldstein 3rd ed says "First consider holonomic constraints. When we derive Lagrange's equation from either Hamilton's or D'Alembert's principle, the holonomic constraint appear in the last step when the variations in the ##q_i## were considered independent of each other. However, the virtual...- Kashmir
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Classical Physics
-
K
I Independent coordinates are dependent
(This is not about independence of ##q##, ##\dot q##) A system has some holonomic constraints. Using them we can have a set of coordinates ##{q_i}##. Since any values for these coordinates is possible we say that these are independent coordinates. However the system will trace a path in the... -
T
Circular motion of a mass on a string on an inclined plane
(I drew motion in the opposite direction so the object would rotate trigonometrically but it should be the same thing) I have just finished the Kinetic Energy and Work chapter in my course and this is the last problem from the problem set. I have not worked many problems with the Work-Kinetic...- ThEmptyTree
- Thread
- Replies: 14
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
T
Conserving Momentum in Emptying a Freight Car
$$\overrightarrow{p_i}=\overrightarrow{0},~\overrightarrow{p_f}=m_c\overrightarrow{v_f}$$ $$\overrightarrow{p_f}-\overrightarrow{p_i}=\int\limits_{t_i}^{t_f}\overrightarrow{F}dt$$ $$t_i=0,~t_f=\frac{m_s}{b}$$ $$m_c\overrightarrow{v_f}=\overrightarrow{F}\frac{m_s}{b}\Rightarrow...- ThEmptyTree
- Thread
- Replies: 54
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Why is the tension in a falling chain not equal to ρgy?
Firstly, There is something I want to clarify. When the system starts moving, parts of the chain that still lies on the table, which have mass ## \frac {(L- y_0)M} {L}##, will be pulled by the force that the hanging chain's weight exert,right? If yes, then : As far as I know, the formula ##F=...- Rikudo
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
I Phase space integral in noninteracting dipole system
Hi all, Consider a system of ##N## noninteracting, identical electric point dipoles (dipole moment ##\vec{\mu}##) subjected to an external field ##\vec{E}=E\hat{z}##. The Lagrangian for this system is...- raisins
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Classical Physics
-
T
Understanding Acceleration and Center of Mass in Shock Absorption
I don't attempt solving a problem until I fully understand it, conceptually. After the hit (when maximum velocity is reached) the person starts losing momentum, having a constant upwards acceleration. The forces acting on the person are gravity and the normal to the ground. $$N - mg = ma$$...- ThEmptyTree
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
V
Books that teach classical mechanics through a discourse method
Books that teaches classical mechanics through a discourse method ie asking interesting questions and answering them maybe a similar one to Understanding Basic Chemistry Through Problem Solving: The Learner's Approach Book by Jeanne Tan and Kim Seng Chan. Not exactly asking numerical questions...- Viishnuuu
- Thread
- Replies: 10
- Forum: Science and Math Textbooks
-
T
Stopping a Bullet: Calculate umin and xf
(a) ##u_{min}=\big(1+\frac{m_2}{m_1}\big)\sqrt{2\mu_k g d}## (b) ##x_f=\sqrt{\frac{2h}{g}\Big(\big(\frac{m_1}{m_1+m_2}u\big)^2-2\mu_k g d\Big)}## Can someone check please?- ThEmptyTree
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
T
Two Pulleys, Two Strings and Two Blocks
Someone pls solve this. I've done it but I'm not sure if it's correct. Thanks!- ThEmptyTree
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
I Trouble simplifying the Lagrangian
Hello, I have posted a similar thread on this question before, but I'd like to get some help to simplify the answers I've got so far in order to match the solutions provided. If anyone could help me, I would really appreciate it. Since (c) is quite similar to (b), I'll leave here what I've done... -
I Trouble understanding coordinates for the Lagrangian
Hello, I'm having some trouble understanding this solution provided in Landau's book on mechanics. I'd like to understand how they arrived at the infinitesimal displacement for the particles m1. I appreciate any kind of help regarding this problem, thank you! -
I Understanding the Coordinates in the Lagrangian for a Pendulum
So I've been studying classical mechanics and have come across a small doubt with the solution provided to the problem in question from Landau's book. My question is: why are the coordinates for the particle given as they are in the solution? I imagine it has something to do with the harmonic... -
B How is the acceleration proportional to the removed force?
Image above is the question. Below image depicts solution. if F1 is removed then the acceleration of that mass must be sum of accelerations of remaining forces. Right?? But answer says that acceleration of that mass is equal to acceleration of F1. I don't understand it. Can someone explain it?? -
T
Tension in rope wrapped around a rod
- ThEmptyTree
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Work & Energy (Question on Classical Mechanics/Slope based Problems)
I used the Change in Kinetic Energy and equated that with the Work Done. The "Work Done" part comprises of two different functions- one is work done by Gravitational Force while the other is the work done by frictional force (or the brakes). /Delta KE (magnitude wise)= 0.5*1350* (20^2)=270,000...- warhammer
- Thread
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

How to find the constant in this indefinite integration?
$$x(t)=\int \dot{x}(t)\mathrm dt=vt+c$$ That's what I did. But, book says $$x(t)=\int \dot{x}(t)\mathrm dt=x_0+v_0 t+ \frac{F_0}{2m}t^2$$ Seems like, $$x_0 + \dfrac{a_0}{2}t^2$$ is constant. How to find constant is equal to what?- Istiak
- Thread
- Replies: 20
- Forum: Calculus and Beyond Homework Help
-

Calculating Velocity when Stuntman Jumps from 1.25m Height
> >A stuntman jumped from $1.25 \ \text{m}$ height and, landed at distance $10 \ \text{m}$. Find velocity when he jumped. (Take $\text{g}=10 \ ms^{-2}$) I had solved it following way. $$h=\frac{1}{2}gt^2$$ $$=>1.25=5\cdot t^2$$ $$=>t=\frac{1}{2}$$ And, $$s=vt$$ $$v=\frac{s}{t}$$ $$=\frac{10 \...- Istiak
- Thread
- Replies: 30
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Why used $\cos\theta$ for $\text{y}$ axis or, gravitational force?
>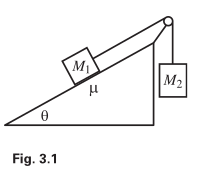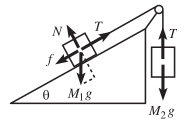<br/> >Mass M1 is held on a plane with inclination angle θ, and mass M2 hangs over the side. The two masses are connected by a massless string...- Istiak
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

How much of the wooden timber was submerged in water?
>Mass of a timber is $20 \ g$. And, density of that timber is $0.27 \ g/cc$. That timber was bind to a metallic materials and, it was released to $0.970 \ g/cc$ water. How much the wood was submerged in water? I was trying to solve the problem following way. $$F=Ah\rho g$$ $$=V\rho g$$ $$=V \...- Istiak
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

I Total angular momentum of a translating and rotating pancake
I have read Classical Mechanics book by David Morin, and there are some parts that I do not understand from its derivation. Note : ## V## and ##v## is respectively the velocity of CM and a particle of the body relative to the fixed origin , while ##v'## is velocity of the particle relative to... -

Tricky conceptual Projectile motion question
So far all I have determined is the equations of motion for the two and that is as follows. It is trivial that y(t)=v1sin(Q)t -gt^2/2 and that x(t)=v2cos(Q)t. Now the angle that is anticlockwise from the negative horizontal of the robber is 90 - Q using basic trigonometry, using this we can...- Rubberduck2005
- Thread
- Replies: 14
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

I Verse from "A Brief History of Time"
1.One can now see why all bodies fall at same rate: A body of twice the weight will have twice the force of gravity pulling it down, but it will also have twice the mass. According to Newton’s second law these two effects will exactly cancel each other, so the acceleration will be same in all...- rudransh verma
- Thread
- Replies: 22
- Forum: Mechanics
-
L
I Help with Goldstein Classical Mechanics Exercise 1.7
I'm trying to solve the Goldstein classical mechanics exercises 1.7. The problem is to prove: $$\frac{\partial \dot T}{\partial \dot q} - 2\frac{\partial T}{\partial q} = Q$$ Below is my progress, and I got stuck at one of the step. Now since we have langrange equation: $$\frac{d}{dt}... -
A
I Time derivative of the angular momentum as a cross product
I am trying to find the equations of motion of the angular momentum ##\boldsymbol L## for a system consisting of a particle of mass ##m## and magnetic moment ##\boldsymbol{\mu} \equiv \gamma \boldsymbol{L}## in a magnetic field ##\boldsymbol B##. The Hamiltonian of the system is therefore... -
E
What is the tension of the rope?
I have attached two different attempts to solve this problem. They both look correct to me but they give two different answers! Which one is correct, which one is wrong and why?- Ebi
- Thread
- Replies: 54
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Symmetries in Lagrangian Mechanics
In Classical Mechanics by Kibble and Berkshire, in chapter 12.4 which focuses on symmetries and conservation laws (starting on page 291 here), the authors introduce the concept of a generator function G, where the transformation generated by G is given by (equation 12.29 on page 292 in the text)... -
Building a motorcycle, need classical mechanics help
Hi! I am an engineering graduate that took my bachelor's degree in Mechanical Engineering much too long ago, but I have forgotten a lot of the classical mechanics/mechanics of materials theory that I had learned many years ago. I am building a motorcycle right now, and I want to calculate the...- Feroyn
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Mechanical Engineering
-

Analyzing an Angular Impulse Problem
What we know: The ball is dropped at the tip A with some speed ##v_0## and rebounds with speed ##v##. This collision produces an angular impulse, changing the angular momentum of the bar with the flywheels. Solution inspired by an answer provided by @TSny in the similar question. Angular...- PiEpsilon
- Thread
- Replies: 12
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

Question on Moment of Inertia Tensor of a Rotating Rigid Body
Hi. So I was asked the following question whose picture is attached below along with my attempt at the solution. Now my doubt is, since the question refers to the whole system comprising of these thin rigid body 'mini systems', should the Principle moments of Inertia about the respective axes...- warhammer
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
D
Finding the period of an orbit ##r=a(1+\cos\theta)##
I've already found the potential and force that produce the given orbit. my results were: ##V=-\frac{al^2}{mr^3}## ##\vec{F}=-\frac{-3al^2}{mr^4}\hat{r}## Now, I've been trying to find the period using the equation ##t=\sqrt{\frac{m}{2}}\int_{r_0}^{r}\frac{dr'}{\sqrt{E-V_{eff}}}## Using...- Davidllerenav
- Thread
- Replies: 26
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help