- #1
Earnest Guest
- 66
- 6
I'm looking at a velocity chart of the Coma Cluster:
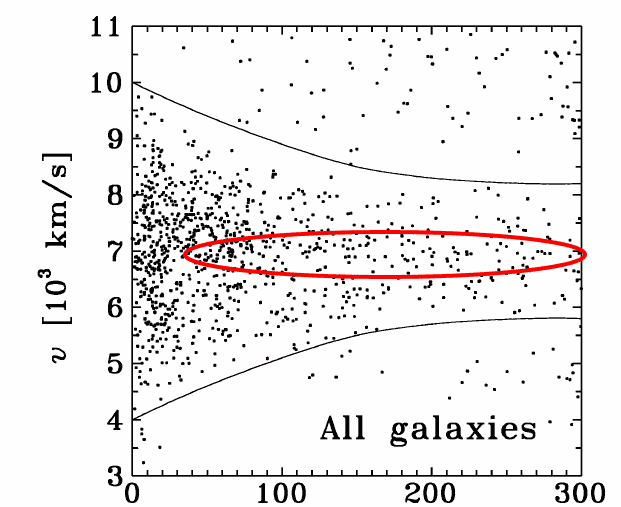
And the question occurred to me: why are there so many galaxies that have a zero velocity (relative to the core of the Coma Cluster which is roughly 7,000 km s-1)? At a distance of a Mpc or two you would expect to find galaxies at the peak of their red or blue shift if they were in orbit. How can they be traveling at the same speed as the core at these distances and still be part of the cluster? What am I missing?
And the question occurred to me: why are there so many galaxies that have a zero velocity (relative to the core of the Coma Cluster which is roughly 7,000 km s-1)? At a distance of a Mpc or two you would expect to find galaxies at the peak of their red or blue shift if they were in orbit. How can they be traveling at the same speed as the core at these distances and still be part of the cluster? What am I missing?