- #1
Avi_R
- 5
- 0
I had a question given, regarding the basicity of certain sites on a molecule. For example, glycine:
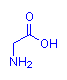
How would you determine whether the OH end or the NH2 end would be more "basic", or the first to get protonated?
How would you determine whether the OH end or the NH2 end would be more "basic", or the first to get protonated?