- #1
agusb1
- 7
- 1
- Homework Statement
- A vaulter holds a 29.4 N pole in equilibrium by exerting an upward force with her leading hand and a downward force with her trailing hand as shown in Figure (included below). Point C is the center of gravity of the pole.
- Relevant Equations
- Sum of forces in y direction = -D + U - Fg = 0
Here's the task:
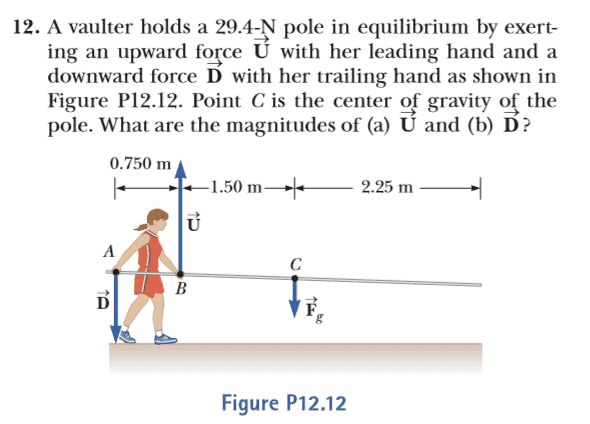
My attempt at a solution (I choose C as an axis):
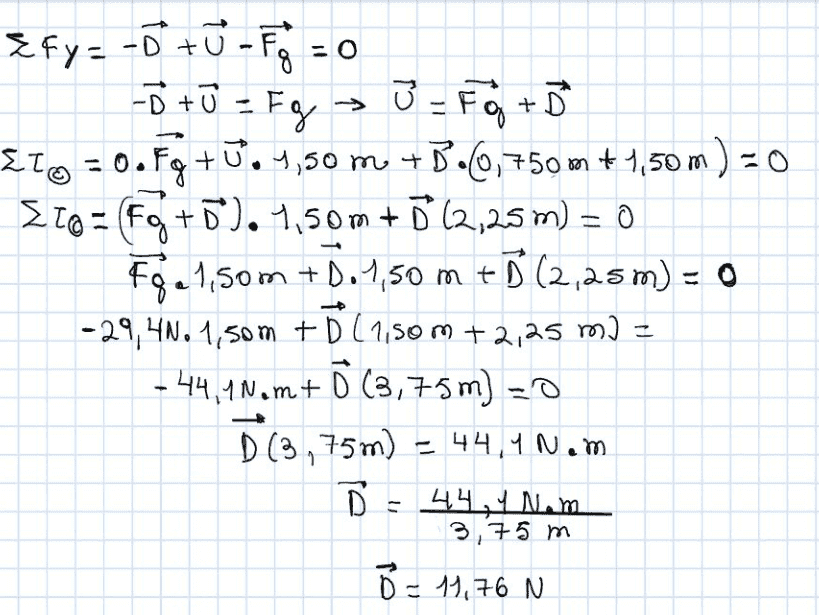
However, the textbook solution says D should be 58.8. What am I doing wrong?
My attempt at a solution (I choose C as an axis):
However, the textbook solution says D should be 58.8. What am I doing wrong?