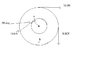
- #1
aaronb
- 23
- 0
Homework Statement
find the net torque on the wheel about the axle through O, taking a = 7.00cm and b = 20.00cm. Assume the positive direction is counterclockwise
Homework Equations
torque = force x distance
torque = force x (radius x sin(phi))
The Attempt at a Solution
10.0 x .2m = -2 (because it's moving clockwise)
9.00 x .2m = -1.8
.07 x 12 x sin(30) = .42
net torque = -3.38 (this is off by 10%-100%)