- #1
mishima
- 570
- 36
Hi, on page 23 of this datasheet (http://www.fairchildsemi.com/ds/LM/LM7805.pdf) the top figure 10 shows a setup for a fixed output regulator, for example suitable for logic chips which need a steady 5V. I was wondering how critical the values of capacitance were for C1 especially and also C0. I was also wondering how in theory these ideal values were calculated for this setup.
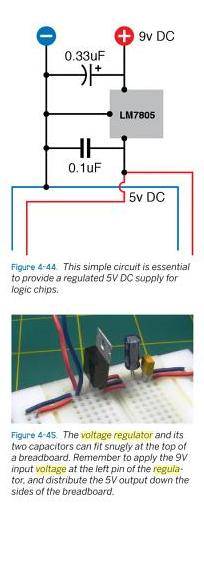
Here is another image from the book "Make: electronics" (taken from google) which shows the setup on top of a breadboard ready for logic chip experimentation. Not surprisingly the same capacitance values are suggested.
Based on the fine print on the datasheet I'm assuming the primary function of C1 is to filter noise from a nearby power supply. I don't own a .33 uF capacitor but could reach that value by combining other values, but I'm wondering if for example a .47 uF or .22 uF would perform just as well, rather than cluttering things up. Thanks.
Here is another image from the book "Make: electronics" (taken from google) which shows the setup on top of a breadboard ready for logic chip experimentation. Not surprisingly the same capacitance values are suggested.
Based on the fine print on the datasheet I'm assuming the primary function of C1 is to filter noise from a nearby power supply. I don't own a .33 uF capacitor but could reach that value by combining other values, but I'm wondering if for example a .47 uF or .22 uF would perform just as well, rather than cluttering things up. Thanks.