- #1
ChEmWen
- 2
- 0
1. The problem statement
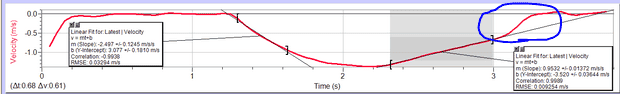
So I am currently working on an velocity/acceleration lab. My physics teacher requires each lab group to find an extension that goes above and beyond the question that we are supposed to answer with the lab. Each group also needs evidence to prove the extension.
That being said, the above picture is a graph of a "shake'n'go" car (a toy car that when you shake it, it moves) created using a motion detector through. As you can see the car accelerates, then decelerates. The graph looks nice, however at the end of the curve, right when the car comes to a stop, the V v T graph shoots right up to 0 (as circled in the picture).
Our lab groups extension is to figure out what that means, but we can not seem to find any sort of explanation to this.
If anyone could provide information on why this is happening (attached documents or links would work or just a simple explanation), it would be hugely appreciated. THANK you so much!
So I am currently working on an velocity/acceleration lab. My physics teacher requires each lab group to find an extension that goes above and beyond the question that we are supposed to answer with the lab. Each group also needs evidence to prove the extension.
That being said, the above picture is a graph of a "shake'n'go" car (a toy car that when you shake it, it moves) created using a motion detector through. As you can see the car accelerates, then decelerates. The graph looks nice, however at the end of the curve, right when the car comes to a stop, the V v T graph shoots right up to 0 (as circled in the picture).
Our lab groups extension is to figure out what that means, but we can not seem to find any sort of explanation to this.
If anyone could provide information on why this is happening (attached documents or links would work or just a simple explanation), it would be hugely appreciated. THANK you so much!