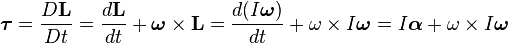- #1
Distance31
- 1
- 0
I am a college student currently working on a physics project involving gyroscopes. Using the equation below (taken from Wikipedia), am I correct in assuming that dL/dt is the torque of the flywheel and that ω x L is the torque of the gyroscope around the axis of precession?