- #1
longcatislong
- 13
- 0
Homework Statement
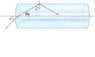
The figure below shows a ray of light entering one end of an optical fiber at an angle of incidence i = 51.0°. The index of refraction of the fiber is 2.05.
Diagram link: http://www.webassign.net/walker/26-55.gif
(a) Find the angle the ray makes with the normal when it reaches the curved surface of the fiber.
Homework Equations
Snell's Law: niSinThetai=ntSinThetat
The Attempt at a Solution
I found theta c (critical angle) to be 29.19 degrees, which correct as verified by my online homework. Then I tried answering part a using niSinThetai=NtSinThetat and got 22.27 degrees as my answer for part a). Online HW system says that's wrong.
Any help is much appreciated! Please tell me what I'm doing wrong and put me on the right track!