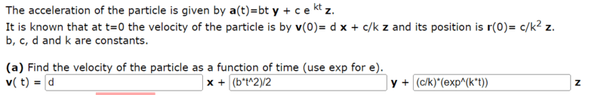- #1
yesmale4
- 41
- 1
- Homework Statement
- The acceleration of the particle is given by a(t)=bt y + c e kt z.
It is known that at t=0 the velocity of the particle is by v(0)= d x + c/k z and its position is r(0)= c/k2 z.
b, c, d and k are constants.
- Relevant Equations
- v\left(t\right)=\int \:a\left(t\right)dt
this is how i try to solve it:
can someone please help me with that because i don't know what I am doing worng here.