- #1
chetzread
- 801
- 1
Homework Statement
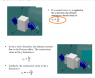
the tensile force is applied at x direction to the cube , the cube will decrease in size in y and z direction , right ?
according to notes,
the strain in x direction εx = σxy/ E , where σy = normal stress in y direction , [/B]
Homework Equations
The Attempt at a Solution
Which is correct ? I think the εx = σx / E make sense , so i think it's correct , because the force is applied in x direction .
Correct me if i am wrong
Attachments
Last edited: