- #1
385sk117
- 50
- 0
Homework Statement
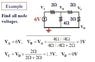
Find the node voltage
Homework Equations
Va = Vb x R1/(R1+R0)
The Attempt at a Solution
I didnt have the original picture of the question but this example is exactly same as the question that i had to solve. but I don't understand this thing from the first step.
How can Vb = Va x (4//4)/(4//4+2)? I know that the 2ohms at the right side of circuit can be added as series and functions as 4ohm and it is paralle to 4 ohm in the middle. and so the total resistance of the circuit is 4//4 +2, but why do we use 4//4 to find Vb? isn't it just 2ohm in front of Vb that we have to use?
Help please
Thanks