- #1
- 6,888
- 2,325
robphy submitted a new PF Insights post
Relativity on Rotated Graph Paper
Continue reading the Original PF Insights Post.
Relativity on Rotated Graph Paper
Continue reading the Original PF Insights Post.
I can draw Minkowski diagrams, but I never found them very helpful compared to just using the formulae, based on the covariant Minkowski-space formalism. My main trouble with Minkowski diagrams is that I have to forget the intuition we are used to from elementary school on interpreting the "paper plane" as a Euclidean plane.pervect said:I've noticed many PF posters seem to have difficulties in drawing space-time diagrams (or perhaps it's just reluctance?). I'm not sure how to interpret this. I often suggest drawing time lines of events as a warm up exercise, hopefully that is a familiar exercise that will get across the abstract notion that one not only can draw a diagram that represents time, one has probably already done so in the past. I'm not sure if anyone has ever taken me up on my suggestion though, or if it's helped any.
vanhees71 said:I can draw Minkowski diagrams, but I never found them very helpful compared to just using the formulae, based on the covariant Minkowski-space formalism. My main trouble with Minkowski diagrams is that I have to forget the intuition we are used to from elementary school on interpreting the "paper plane" as a Euclidean plane.
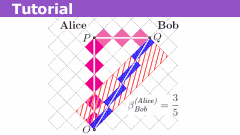
Relativity on rotated graph paper is a visual representation of the principles of relativity using a two-dimensional graph paper that has been rotated at an angle.
Einstein's theory of relativity states that the laws of physics are the same for all observers, regardless of their relative motion. Relativity on rotated graph paper helps to illustrate this concept by showing how different frames of reference can lead to different observations on the same graph paper.
Relativity on rotated graph paper can be applied in various fields of science, such as physics, astronomy, and engineering. It can help in understanding the behavior of objects in motion, the effects of gravity, and the properties of space and time.
Rotation of the graph paper changes the orientation of the axes, which can affect the measurements and observations made on the graph. It also allows for the visualization of different frames of reference and their relative motion.
While relativity on rotated graph paper can be a useful tool for understanding relativity, it is important to note that it is a simplified representation and does not fully capture the complexities of Einstein's theory. It also may not be applicable in all scenarios and should be used in conjunction with other methods of understanding relativity.