- #1
basty
- 95
- 0
Please take a look below example (the attached image below).
How do I know that the angle ##\sin (\frac{7π}{4})## is corresponds to the coordinates ##(\frac{\sqrt {2}}{2}, -\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2})##?
I know that ##\frac{7π}{4}## is 315°.
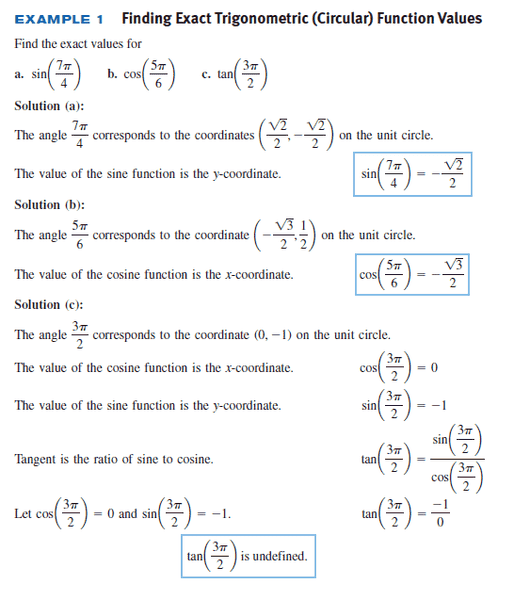
How do I know that the angle ##\sin (\frac{7π}{4})## is corresponds to the coordinates ##(\frac{\sqrt {2}}{2}, -\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2})##?
I know that ##\frac{7π}{4}## is 315°.